20 Bright Siders Share Stories That Prove Children Live to Tell the Truth to Anyone They Meet


Most people have 12 pairs of rib bones, which means 24 ribs in total. But, some have 25. One in 200 people is born with the so-called cervical rib. It forms right above the first rib and grows at the base of a person’s neck, above the collarbone. A cervical rib can be located on the left, right, or both sides.
You can have it without even knowing about it. This extra rib doesn’t necessarily form completely. It can be just a thin strand of tissue fibers not even an X-ray can see. In most cases, it’s really not a big deal — unless it starts putting pressure on nerves and blood vessels.
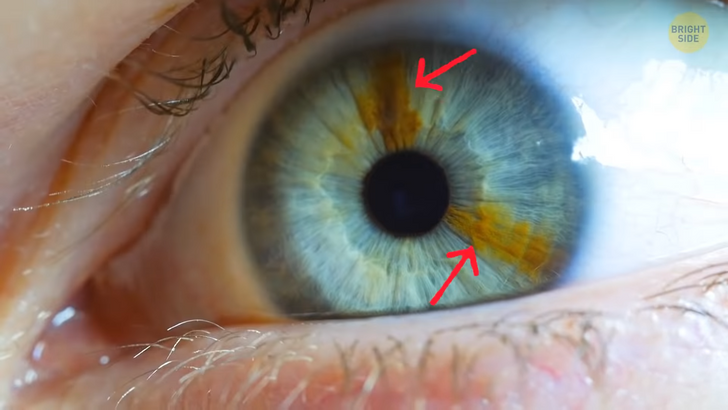
You probably don’t think that much when you’re filling out a form and come across “the eye color” section. But, it’s not that simple for people who have this rare body feature called heterochromia. That’s when a person has a difference in eye color. Complete heterochromia means you have two different colored eyes, like one blue and one brown eye. But there’s also partial heterochromia. It means only a part of your iris is a different color from the rest. In the US, fewer than 200,000 people have it.
Natural red hair is not as common as you might think. Only 2 percent of the world’s population has it. There are 8 genes responsible for it. Scientists used to link it with just one rare and recessive gene that you had to inherit in two versions from both of your parents. Then, they realized not every person with two red-haired versions got red hair. So, there have to be some other genes involved.
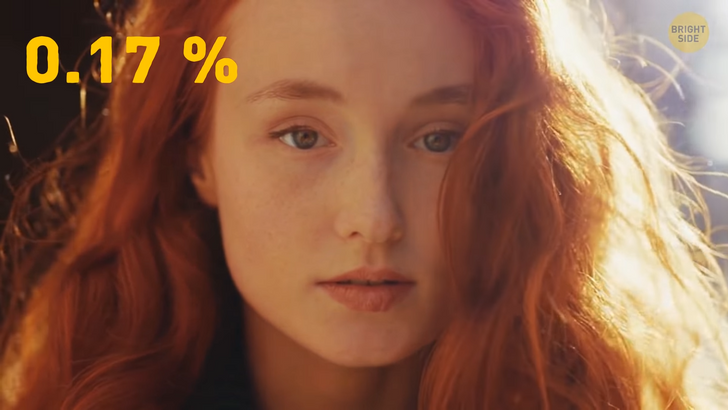
Do you know which eye color is super rare? Gray. Most people have either brown, blue or hazel eyes. About 17 percent of people have blue eyes, but the odds of getting those and red hair at the same time are just around 0.17 percent. Less than one percent have gray eyes. If you have gray eyes, it’s because of a low level of melanin in the front layer of your iris.
There are just 43 people in the world that have this extremely rare body feature called “golden blood.” About 0.6 percent of Americans are AB-negative, but this is still not the rarest type in the world. In 1961, scientists discovered there was an indigenous Australian with a specific blood type — the type that completely lacks certain antigens, which means proteins or red blood cells. Those who have that exclusive type can donate to others with rare blood types but can receive it only from one of those other 40-ish people who have it. That’s why it’s “golden blood” — it’s worth its weight in gold.
Another rare body feature is a small hole near the ear. At first, it seems like some sort of gill. Some scientists have a theory it could be some sort of evolutionary remains from times when we were aquatic creatures. This tiny hole is mostly present near one ear, not both.
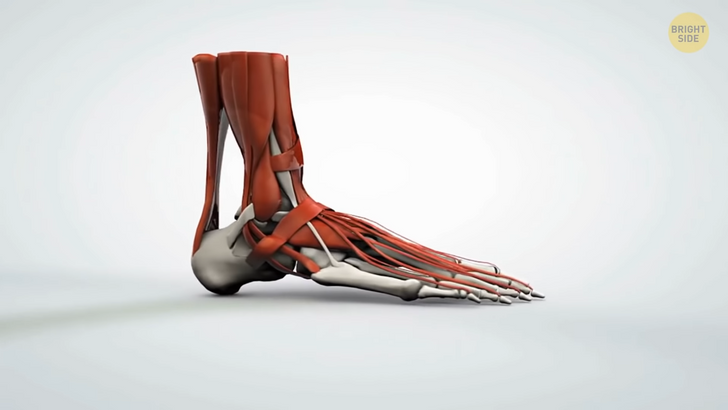
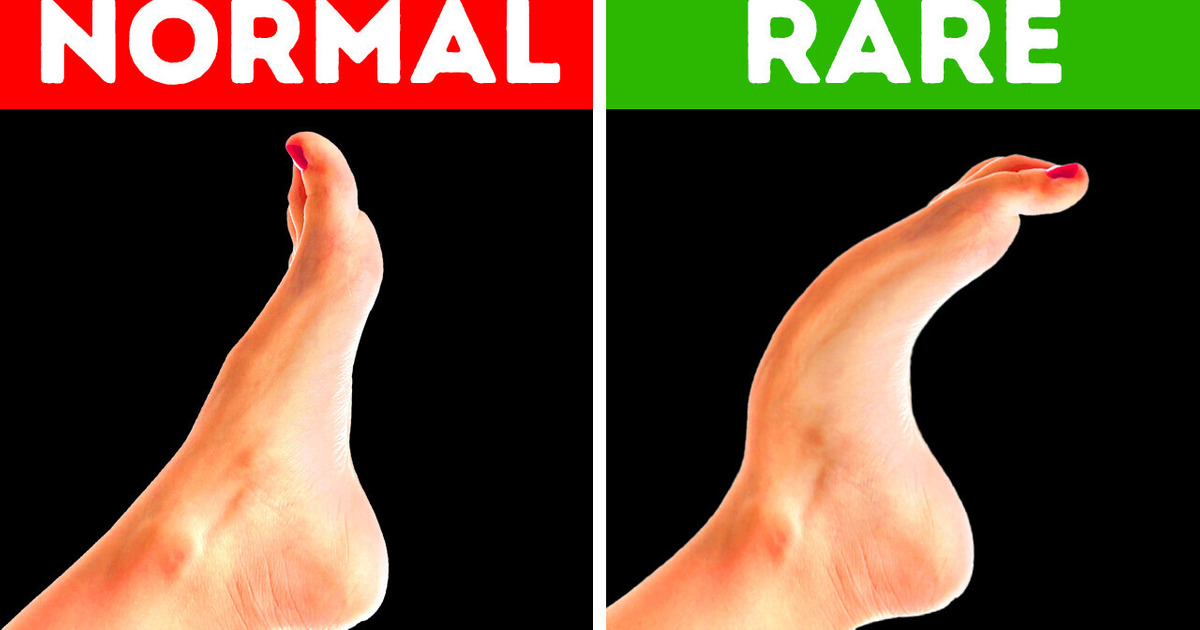
Some people have chimp-like feet. They’re bendy, flexible, and adapted for climbing trees. Researchers at Boston University filmed 400 people walking barefoot and concluded that 1 in 13, or 8 percent of the participants, had this feature. Typically, the human foot is rigid. We’ve evolved that way, so we can efficiently walk on even terrains — at least, that’s something you could learn from textbooks. But, other apes have flexible feet. This allows them to grasp branches as they move through the trees.
The kind of foot that’s similar to tree-dwelling apes is flexible in the middle. It bends at the ball of the foot and is halfway between the ball and the heel. Human feet normally have a joint at this point. But, the majority of people have stiff ligaments that span the joint. That’s how they keep it rigid. Those rare people with chimp-like feet have softer ligaments that allow their mid-foot to bend.
Try to move your middle finger or your pinky. It’s hard to do it without bending your ring finger, right? That’s how it works for most people. But, there are some who can completely isolate their ring finger. Researchers believe it’s hereditary.
If you can touch your nose or chin with your tongue, it means you stand with around 5 percent of the world’s population that can do that. Most people’s tongues won’t reach that far out, no matter how hard they try.
Some women have super color vision. With this, you are able to see and distinguish colors thanks to special cells in your eyes called cones. People usually have three types of cones. But, scientists are especially interested in tetrachromats. They believe these people have 4 types of cones. Thanks to that, they’re able to see 100 million different colors.
One research team from Newcastle University spent years searching for such people. Finally, in 2010, they found one of them. It sounds like a magic power at first, but it’s not always fun. One tetrachromat said going to the grocery store can be a real nightmare because it’s like seeing a trash pile of colors coming in at every angle.
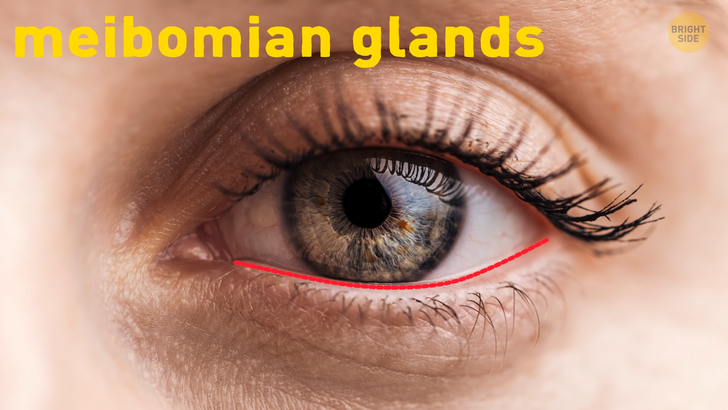
There are people born with a double row of eyelashes. That extra row emerges from the ducts of meibomian glands. One of the celebrity examples of such a rare genetic mutation was Elizabeth Taylor.
Here’s something you can try. Move your right foot off the ground. Go in a clockwise direction. Can you draw the number 6 with your big toe? No pencil or paper allowed — just your toe. The majority of people will soon notice they’ve started moving their foot in the opposite direction, without even realizing it. This partially happens because the number features a counter-clockwise circle. Only in some rare cases, when either the brain is wired in a different way or thanks to practicing, can some people do it the other way around.

You’ve probably also heard that myth that it’s not possible to sneeze with your eyes open. Well, it is. There are cranial nerves that link your eyes and the nose. That’s the reason why, when sneezing, most people automatically close their eyes. But it’s still possible to sneeze with your eyes open, and nope, your eyes won’t pop out because of it.
There are people who can make a roaring noise in their heads. All they have to do is tense their ears or jaws. We all have this small muscle in our ears. Its role is to silence certain sounds that can really distract you, for example, when you’re chewing. And some have the ability to flex that tiny muscle. That way, they create an audible rumble like there’s a small lion roaring inside their head.
Can you bend your thumb backward? Then, you must have something called Hitchhiker’s Thumb. It’s a double-jointed thumb that allows them to bend it backward. There’s no risk in doing this, and it’s not something very uncomfortable for them. It’s possible thanks to distal joints within the thumb. In some cases, people can move only one thumb backward, while others can move both.
There’s a rare body feature that turns some people into “super-tasters.” Genetics plays a role in many things, including our taste buds. Approximately 25 percent of the world’s population is in the category of super-tasters.
Compared to regular tasters, they have more visible tiny dots on the tongue, called taste papillae. It makes them more sensitive to certain tastes, like those that are sweet, bitter, and salty. They have more pain receptors than average, which is why they’re not that into spicy food. Also, they most likely won’t eat that many vegetables since the taste will be too bitter for them.
Wisdom teeth used to be important once, and we don’t quite need them anymore. But their absence is actually a pretty rare body feature. These days, when wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, try to break through the gums, in many cases, they run out of space. As a result, it can get overcrowded inside your mouth. So, many people have to get rid of those “extra” teeth — about 5 million people every year, to be precise.

Synesthesia is the phenomenon when a brain mixes up certain senses. So, a person with synesthesia is able to taste music or hear colors. People say Mozart had it. For instance, he’d see D major as a warm orangey sound and B-flat minor as blackish. This condition is rare — approximately 1 in 2000 people have it, and the majority of those are left-handed or women.
Imagine you can recall what you were having for breakfast 15 years ago like it was yesterday. Sure, you keep some special memories, but there are people that can recall everything that has happened to them till now as clearly as they recall things from this morning. If you give them a certain date, they’ll be able to tell you what they did and where they were in the slightest detail. It’s called highly superior autobiographical memory, and only 60 people on the planet have it.