12 Stories That Prove Kindness Is the Strongest Armor


Try not to wear the same pajamas for several nights in a row. Otherwise, bacteria and the skin cells your body sheds will collect in your clothing. And then, even if you regularly wash and change your bedding, it won’t stay clean and fresh for long. Your pajamas will transfer all that yucky stuff to your bedsheets.
Plus, people often sweat while sleeping. Their sleepwear absorbs all that sweat. And this creates a perfect playground for bacteria. They adore dark, moist places. And nothing will make them happier than producing bad smells and disturbing your sleep!

That’s why crawling to bed in sweaty pajamas can make you restless. Even worse, you might start to feel itchy all over. At the same time, fresh sleepwear and bed linen can help you relax, so you can wake up refreshed. If you don’t have insomnia, you’ll spend around one-third of your life asleep. But there are creatures that sleep even more. For example, for a dog, it’s 44% of their life. And for a python — 75%.
If you catch yourself clenching your jaw because of stress, put it to work instead! Munch on an apple, a carrot, or trail mix. It’ll distract you and help you to wind down.
Researchers have discovered that people from different countries and cultures have the same dreams. The most common ones that occur across the world include falling and being chased. People also dream about flying, arriving late, feeling cold, and being unable to move.
Your most vivid dreams occur during the REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. This stage repeats in short episodes throughout the entire night. Such episodes are usually an hour and a half or two hours apart. By the way, there’s a theory that while sleeping, you don’t have a single dreamless moment.

Some kinds of eye movements during REM sleep correspond to certain events happening in your dreams. It means that at least a part of the dreaming process is similar to watching a movie. You see longer dreams in the morning hours. And each next episode of REM sleep lasts more than the previous. That’s one of the reasons why you’re more likely to remember your dreams on weekends when you can afford to sleep in.
Your dreams look so realistic thanks to your brain. Its job is to create an adventure or specific environment in your dream. To do this, the brain uses all kinds of sensory data. That’s why the picture often looks confusingly realistic. Your brain contains more than 86 billion nerve cells. And all of them are joined with one another by 100 trillion connections! That’s way more than the number of stars in our home Milky Way Galaxy!
But if you didn’t believe that and decided to count all those nerve cells in your brain, it’d take you up to 3,000 years. Your brain can easily get bored. A study has discovered that every 10 minutes, it needs some emotional jolt. It’s crucial for resetting your attention. People are the only mammals that can and DO delay sleep willingly.
It’s impossible to “catch up” on sleep. A Harvard study has shown that trying to compensate for sleep negatively influences your ability to focus and makes your reaction time longer. Your dreams are a complex mixture of your imagination, memories, and knowledge. The average person has from 4 to 7 dreams every night. But not all people remember them.
However well you rest, you’re bound to feel at least a bit tired at two completely different times of the day: 2 PM and 2 AM. That’s when a natural dip in alertness happens. It’s totally responsible for your irresistible desire to have a post-lunch nap. During REM sleep, you can start to act out your dreams. [subscribe] That’s why your brain temporarily paralyzes your muscles during these periods. Otherwise, you may accidentally hurt yourself.
If you mix five tablespoons of cane sugar and two tablespoons of sea salt, you’ll have fewer problems with sleep. Just put a bit of this mixture under your tongue before going to bed. There’s an opinion that falling asleep at night should ideally take from 10 to 15 minutes. If you need less than 5 minutes to crash out, you’re likely sleep-deprived.

A 2015 study suggested that people with their beds surrounded by clutter had more problems with sleep. It turns out what you see when walking into the room can influence how fast you fall asleep. There’s evidence that not only people but also animals (and even some insects) can have problems with sleep! In this case, they begin to put on excess weight, become clumsy, and often start to lose their balance.
These are the same symptoms people with sleep-deprivation have. If you can’t fall asleep, go blow some soap bubbles! This process resembles a deep breathing exercise. It’ll effectively take your mind off whatever anxious pre-bedtime thoughts you’re having. One study claims that in your dreams, you can only see the faces you already know or have seen on TV or social media.
If you want to sleep better at night, try to get as much natural sunlight during the day as possible. It’ll both make you more energetic in the daytime and improve the quality of your sleep. People only using 10% of their brainpower is just a myth. Even when you’re resting or sleeping, more than a tenth of your brain is working. Admittedly, not all of its regions are active around the clock. But most of them work on this or that task 24/7.

Regular physical exercise helps you to fall asleep faster and more easily. It also makes your sleep better. At the same time, if you exercise right before going to bed, you’ll most likely have problems drifting off.
Putting on a pair of socks can help you fall asleep. When you warm up your cold feet, your blood vessels become wider. Your brain perceives it as a signal it’s bedtime. Within 5 minutes after waking up, you forget 50% of your dreams. Five more minutes — and 90% of the memories are gone.
It likely happens because you start to use your brain much more as soon as you’re awake. And it doesn’t have enough resources to get you through the day AND remember everything you saw in your dreams at night.
To wind down in the evening, try to make your home dimmer. Opt for soft-light lamps or even candles instead of switching on bright overhead lights. Indirect light not only creates a calmer setting but also doesn’t mess with your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.

Many of your dreams are rather bizarre (and don’t try to deny it!). That’s because the part of your brain responsible for making sense shuts down when you’re dreaming. On average, when a person snores, it doesn’t get louder than 60 decibels. That’s as loud as a regular conversation. But sometimes, the noise level can reach 80 decibels. And this is as loud as a working food blender!
You dream in pictures. This means most of your dreams are visual, with few sound effects and little movement. The human brain doesn’t form completely until age 25. And curious thing: its development starts from the back and then continues toward the front. It means that your frontal lobes, which are in charge of reasoning and planning, are the last to “mature.”
If you can’t drift off however hard you try, start to replay your day in reverse. Think about what you had for dinner. Then about how you got home from work. Recollect what happened in the office and how you spent your afternoon. Trying to remember even the tiniest details is usually boring enough to make you doze off.
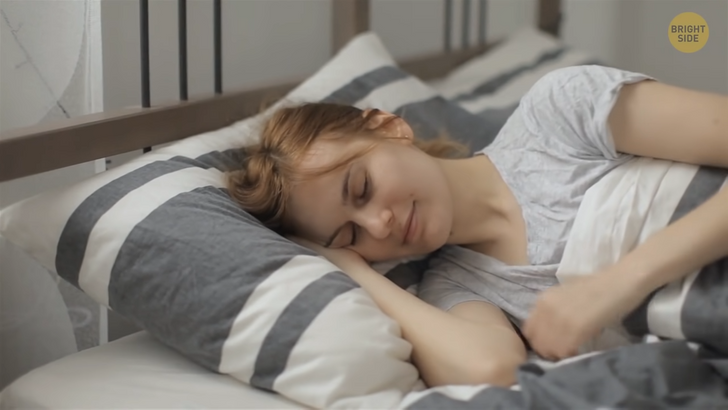

Some sleep experts claim there’s a direct link between your personality and your favorite sleeping position. For example, those who prefer resting on the stomach with their hands by the pillow and the head turned to the side tend to be bold and outspoken. They also don’t take kindly to criticism.
A person who sleeps on their side with the knees bent toward the chest is likely to be sensitive and a bit shy. And those who sleep on their back in the starfish position are selfless people always ready to help. Sleep experts are sure that people who smell lavender before going to bed or have it nearby during the night have fewer problems with sleep. A scented candle will do too.
However counter-intuitive it may sound, plunging your face in a bowl with ice-cold water can help you fall asleep. At first, it’ll shock you even more awake. At the same time, it’ll reset your nervous system. Freezing water will trigger a reaction lowering your blood pressure and heart rate. It’ll make you relaxed, refreshed, and ready for bed.











