I Refuse to Sacrifice My Retirement Dream for My Unemployed Son

You may have this rare body feature already and not know about it since sometimes even an X-ray can’t spot it! Most of us have 12 pairs of rib bones, which means we were born with 24 ribs. There are some folks, though, that actually have 25 ribs! Only one in 200 people have this rare extra feature, and it’s called a cervical rib.
It generally appears above the first rib, right at the base of the neck, and above the collarbone. It’s nothing to worry about, though. Most of the time, they’re unnoticeable, and if ever painful, they can be safely removed.
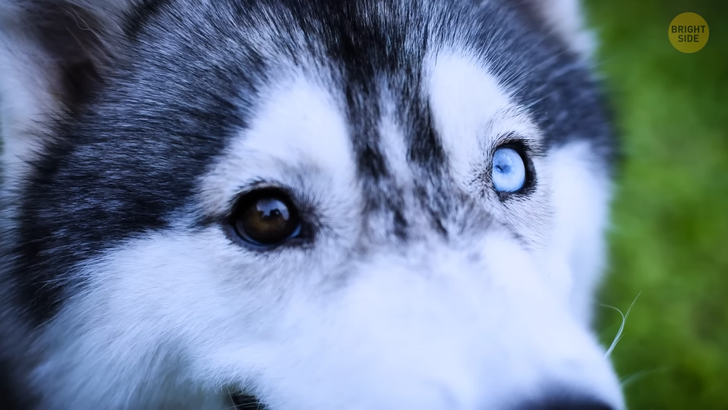

Do you know how huskies can sometimes have their eyes in different colors? Some people come equipped with this rare feature, too! The medical term for it is heterochromia. This name comes from the ancient Greek word “heteros,” which translates to “different” and “chroma,” which means “color.”
People with this condition can either have complete, central, or partial heterochromia. The complete type means that the person has two completely different colored eyes, say, one brown and one green. Two different colors in the same eye are what specialists call central heterochromia. A person with partial heterochromia has just a portion of their eye of a different color.
You can either be born with this condition or get it, say, after an injury. Still, it’s extremely rare! Less than 200,000 people are diagnosed with it in the US. Either way, let’s face it, it does look pretty cool.
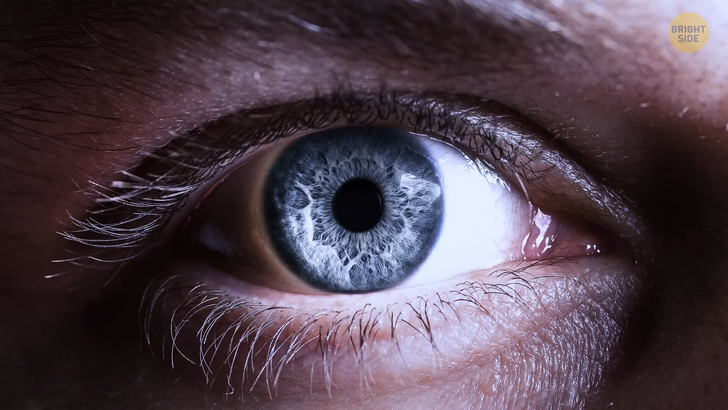

Speaking of eye color, wanna try guessing what the rarest one is? I’ll spare you the Google search. It’s gray. Blue eyes may have been your first thought, and they are indeed already pretty rare. Only around 8 to 17 percent of the world’s population have this eye color.
When it comes to gray eyes, though, they are even more special: less than one percent of people have them. This rare body feature is caused by a lower level of melanin in the eye’s layers. If you’re interested in meeting someone with gray eyes, your best chance is in Eastern and Northern Europe. Even rarer eye colors are red or violet, but these can sometimes be the result of different health conditions.
There are people out there who have the superpower of seeing 100 million different colors without the help of any fancy gadgets. We see colors thanks to some cells in our eyes named cones. Most of us have three types of cones to help “translate” what we see into the colors that our brain is able to understand. However, specialists think there’s a small group of people called “tetrachromats” who have four types of these cones. So far, researchers have only been able to identify women with this condition.
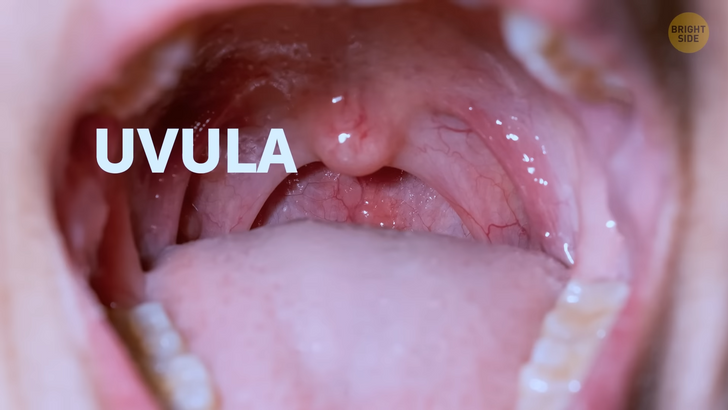
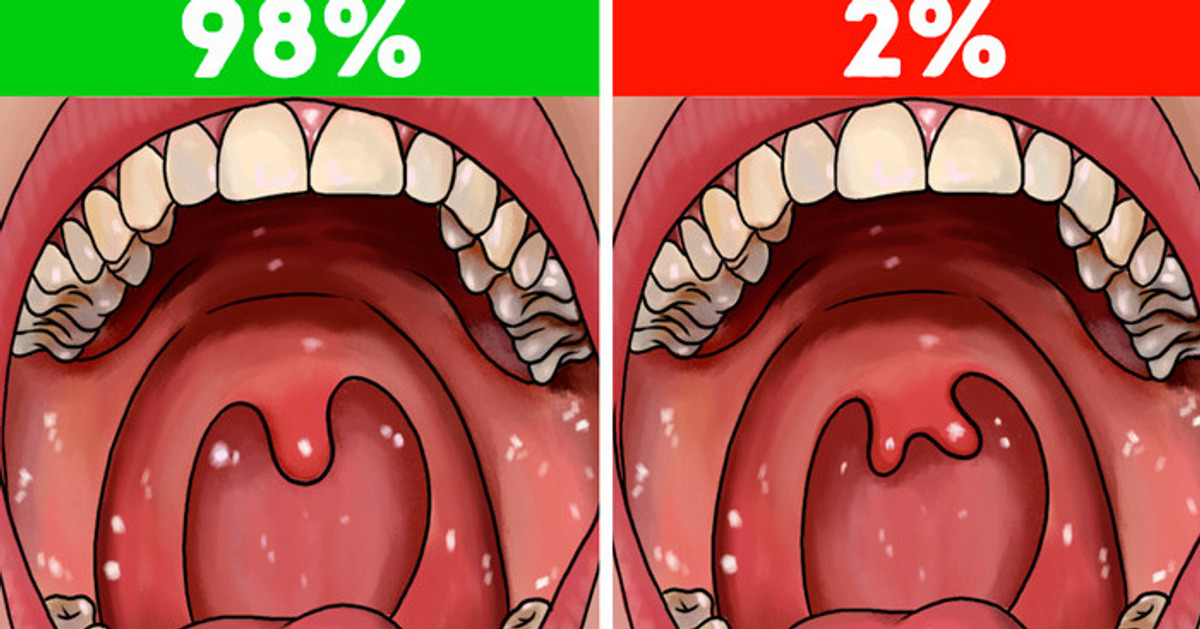
That little teardrop-shaped ball hanging there in the back of your neck — you know, the one that helps with swallowing your food — is called a uvula. The name comes from Latin and translates to “little grape.” Surprisingly enough, around 2% of people are born with a bifid uvula, which means that this indispensable organ in them is either split or forked.
You sure can surprise others with this cool feature of yours at parties. Joking aside, though, people with a bifid uvula may sometimes have trouble eating, drinking, and speaking. They might also have issues with digesting food. Their speech may also sound a bit unusual, but this depends on how much the uvula is split.
This particular body feature might not be the perfect trait when going on vacation, but it does allow people to do more with less sleep. They say that famous people like Nikola Tesla, Margaret Thatcher, and Winston Churchill had this super rare feature.

This gene, called the DEC2 gene, helps with regulating our circadian rhythms. Those are the natural biological clocks that let us know when we should be sleeping or eating by making us sleepy or hungry. A person with this rare mutation can basically go through a normal sleep cycle in less time. They can feel rested even if they slept for only 4–5 hours. That’s one superpower I’d definitely want to have!
How about a gene mutation that gives you superhero-like bones? They are basically unbreakable! It also makes your skin less prone to aging. Yep, looks like, with this feature, you can walk away from accidents unharmed and even withstand the flow of time!
Some other people out there come with a very attractive feature, but it can go unnoticed, at least at first glance. They have a little something called distichiasis, which basically means an extra row of eyelashes. Just in case you’re wondering about the medical aspects, too, it results from a genetic mutation of a certain gene. As beautiful as it may sound, people with that extra eyelashes layer can experience some pretty unpleasant sensations in their eyes and, in some cases, even have problems with their vision.
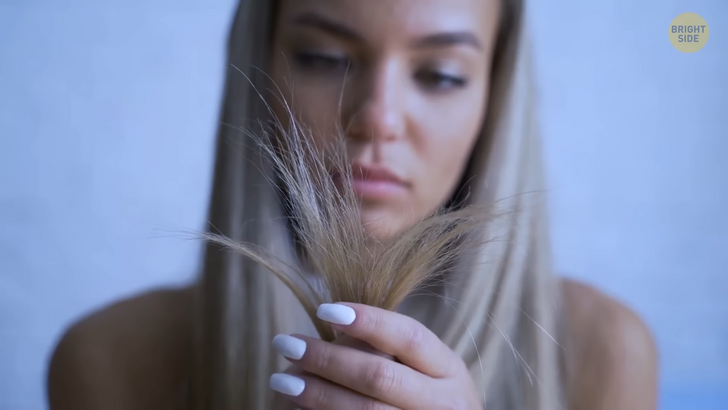

If “spun glass hair” doesn’t ring a bell, know that it is, in fact, a condition you might have. I know it’s pretty self-explanatory, but just FYI, it causes frizzy and dry hair. It’s basically so unmanageable that you literally can’t comb it. It also tends to grow out from the scalp in all directions.
As for coloring, it comes in either bright blond or silver. Most of us have hair strands that are cylindrical. People with this condition have triangular or heart-shaped strands, or even flat altogether. It’s extremely rare, with only 100 confirmed cases, but it does become more manageable with age.
Most of us humans have evolved to have some specific traits depending on the area of the globe that we live in. But there is a group of people — specifically those that live in higher altitudes — that developed some pretty cool traits. Let me explain: high-altitude environments come with less oxygen. Not only do these people survive in these locations, but they’ve adapted to actually thrive out there.
For example, those living in the Andes Mountains of South America have red blood cells that can carry much more oxygen. It makes their overall circulatory system a lot more efficient. People living in similar conditions in other parts of the world have also adapted in their own way. They are able to take more breaths so that they can properly supply their bodies with oxygen.
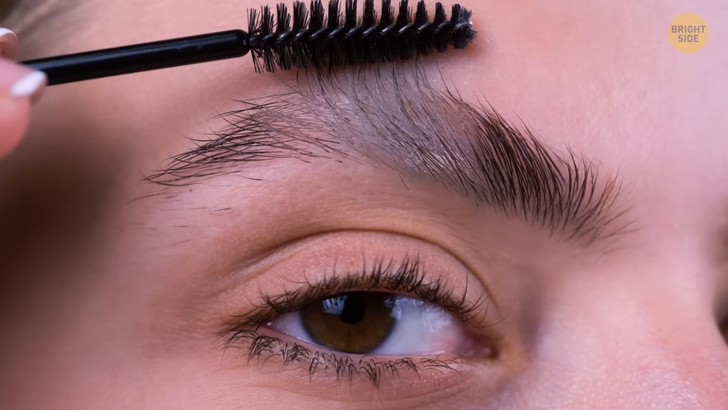

This one is very important when it comes to looks but means little in terms of a person’s overall health. I’m talking about “piebaldism.” Those who have it lack melanocytes — those cells that produce the hair pigment — in some parts of their hair. It’s most common above the forehead in the front of their hairline, but it can also appear on the eyebrows or eyelashes. Folks who have it are born with this condition and carry it throughout their whole lifetime. If you really want to get rid of it, there is always hair dye available, but I personally think it looks super cool!
We all know cilantro really isn’t everyone’s cup of tea. I don’t know about you, but it tastes like soap to me! It turns out it’s not actually a preference but rather a gene that causes the plant to have this vile taste instead. A study performed on a group of about 30,000 people revealed that you can find a particular gene variant in people who say that cilantro tastes “soapy.” This gene has more to do with the odor of the plant than the taste itself.
If you’re one of those people but really want to give cilantro a chance, either way, there is a small trick you can try — or ask the people that cook the meals in your household. You can always crush the herb before using it in dishes. Why does that help? Well, because with crushing, the chemicals that are responsible for the soapy taste are broken down and are less likely to taste unpleasant.











