20 Things That Were Cleaned Up and Can Now Be Put on Display

As the most abundant protein in the human body, collagen makes up about 30% of our total protein content. It's the primary structure for connective tissues including skin, bones, muscles and tendons, providing strength and elasticity. However, our body's natural collagen production inevitably diminishes with age, causing various signs. Recognizing these indicators is crucial for health and supporting collagen levels.
Disclaimer:
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE. SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING
YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS
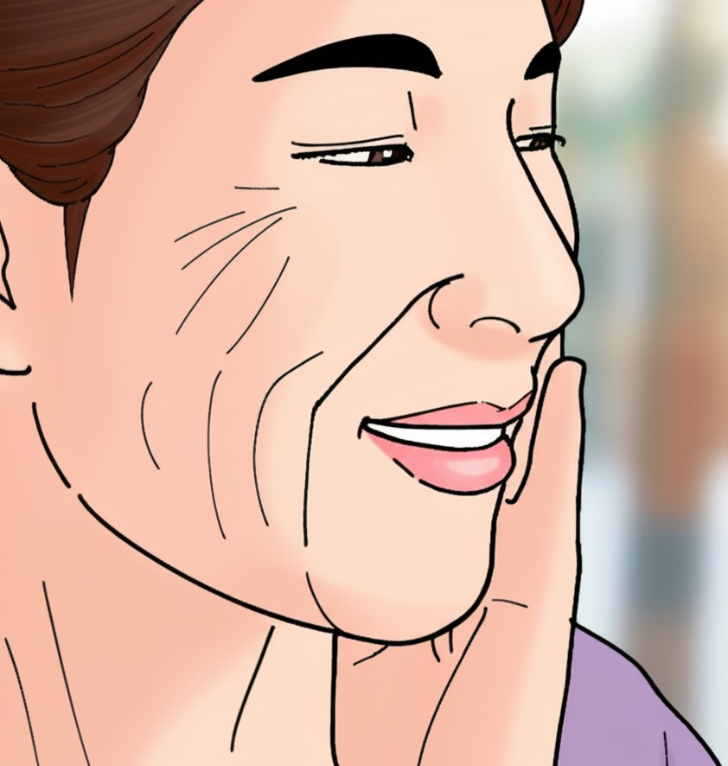

One of the earliest and most noticeable signs of diminishing collagen is the formation of fine lines and wrinkles. As collagen levels decrease, the skin loses its firmness and elasticity, leading to sagging and the development of wrinkles. This process is a natural part of aging, but collagen levels can also be affected by factors such as excessive sun exposure.
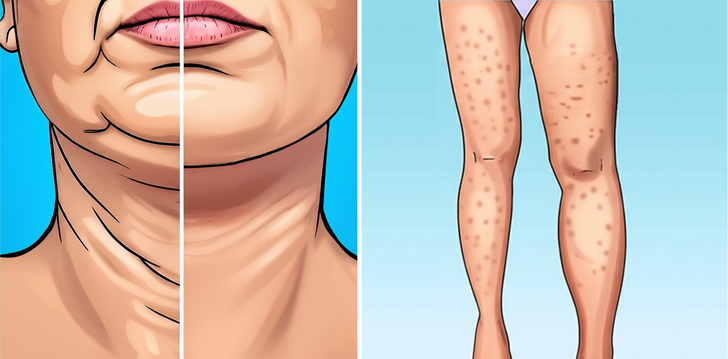
Collagen gives skin its firmness and structure. When levels decline, skin can sag—especially around the cheeks, jawline, and neck—leading to a less youthful look. Low collagen may also contribute to the appearance of 'strawberry skin' and clogged pores, often associated with keratosis pilaris, where enlarged pores create a characteristic bumpy texture. Maintaining collagen helps improve skin smoothness and elasticity.
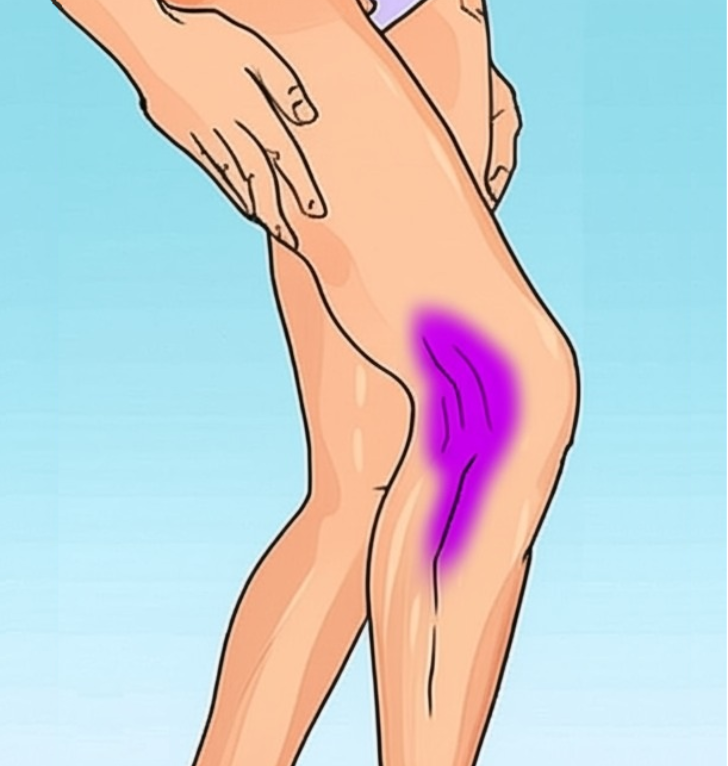
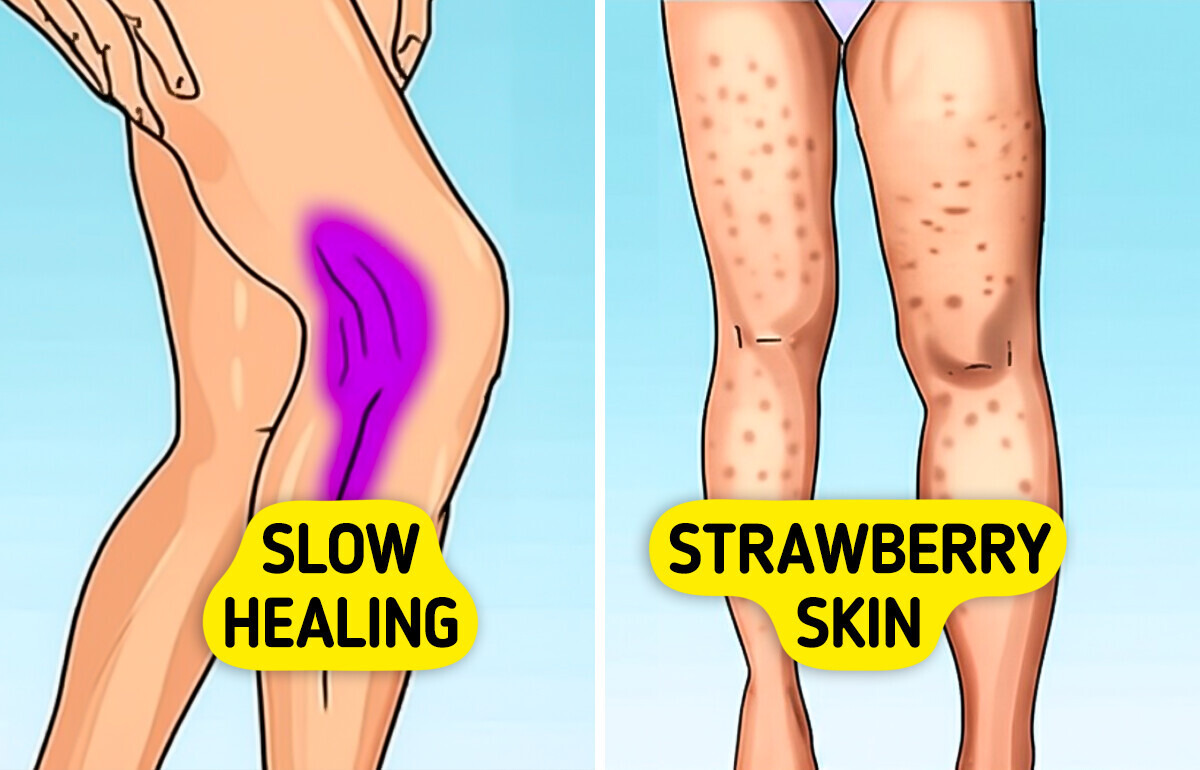
Collagen is integral to the wound healing process. A deficiency can lead to prolonged healing times for cuts, bruises, and other skin injuries. This delayed recovery increases the risk of infections and can lead to more pronounced scarring.
Beyond its role in skin health, collagen is a major component of cartilage—the tissue that cushions joints. A decrease in collagen can lead to joint discomfort, stiffness, and an increased risk of osteoarthritis. Maintaining collagen levels is vital for joint flexibility and overall mobility.
Collagen is present in the lining of the digestive tract, where it supports gut integrity. A deficiency may contribute to digestive problems, including leaky gut syndrome, which can lead to nutrient malabsorption and increased inflammation. Ensuring adequate collagen levels supports digestive health and overall well-being.
Several lifestyle choices can accelerate collagen degradation:
To support and enhance collagen production, consider the following approaches:
Recognizing the early signs of collagen deficiency can empower you to take proactive steps toward restoring your skin’s vitality and well-being. For more insights on identifying important health signals your body may be sending, check this article.











