12 True Stories With Twists So Wild, They Could Break the Internet

You’re walking down the street and notice a QR code right next to a parking meter. You have just parked your car, but for some reason, this QR code is grabbing all the attention. You think to yourself: “Hey, maybe this is how I pay for parking nowadays.” You take out your phone and scan it. A link opens up and redirects you to a fishy-looking site that shows you where you have to pay and is asking you for a lot of money. There’s no one around you to help, and you know for a fact that this is not the price for 2 hours of parking. After going through the procedures, you look at your bank account and are in shock. They took a lot of your money! You call the bank to quickly freeze your account and ask them to help you get your money back.
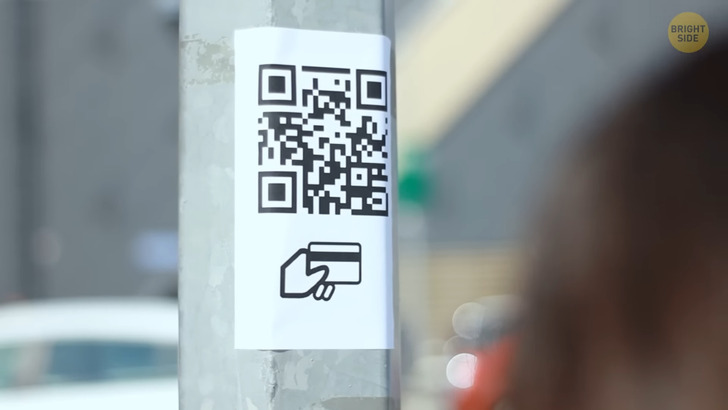

You scratch your head in confusion and look around you. Nobody seems to mind these QR codes scattered all over the city. You show them to other people in the city, and they’re also surprised. QR codes stand for “quick response” codes since they’re easy to scan and get info on something. It only takes seconds to get an insight on something or check out the menu at a restaurant. While this has been an awesome way to make our lives easier, some people are using it for the wrong reasons.
Many experts warn about randomly scanning QR codes off the streets since it may lead to scam websites where people can take your information and bank details and gain access to your credentials, just like what happened when you were trying to pay for parking. So, that QR code that you scanned redirected you to a fake website where you handed out all of your personal information, including banking details. The people behind this scam can now access your account and take out as much money as they want. They might even ask for more details like your email and phone number, which you shouldn’t give out unless you trust the source. You call someone to assist you for them to take down the QR code. On social media, you find out there are dozens of people who are also falling for this trick and losing their money.

This is equally common for people who access public Wi-Fi hotspots. In settings like a café, airport, or public park, you always choose the Wi-Fi network that has the name of the place you’re sitting in. Like FREEWIFICAFE, for example. Without thinking, you instantly connect to the router and are redirected to a page where they ask you to log in with your email, password, and other information about you. Most of the hotspots are legit, but some belong to people who set up this hotspot to lure everybody in to give out their personal information. Once you enter their page, the people on the other side are watching you jot down everything they ask for. They even create a page where you have to fill in extra personal info about yourself like addresses, place of work, and so on.
The best way to properly avoid this is by asking anyone who can assist you and confirming whether or not you’re connected to a safe Wi-Fi network. Or, if you frequently visit the place to do some remote work, always connect to the same Wi-Fi router even though the bad one that was set up has the same password and an identical landing page. You can’t just trust anything in your inbox these days. Especially not the emails that claim you just won something or that someone is contacting you for a fishy business proposal. Such emails are usually presented convincingly and make you think that they’re real. But the best way to spot them is to pay attention to the details of the content. Check for spelling mistakes or style of writing. If it looks like there are some mistakes or weird and unprofessional writing, this can be a red flag. Also, check if the email signature exists.

Most companies have an email signature with the person’s job description and credentials to verify the source. These emails contain links that can redirect you to websites where the people who sent out these emails can get all your information. You should also pay attention to the one sending you the emails to check if they are verified and come from a legitimate source. So, if the email ends with anything other than the company’s name, this can also be a red flag. Sometimes people try to pretend they’re someone you know: your boss or co-worker, or even your friend. They would write to you in a very convincing manner where you would think that they’re actually sending you an email. These sorts of emails may not be real. You should check for the source and the content and verify with the person who sent it to you before replying or giving out any information.
The targets usually include people who have high positions in large companies and corporations. They are considered the big fish in the game. Your emails also include links in which you can give out sensitive information which they can use against you. Protecting yourself online is not easy and requires a lot of concentration and hard work. There are many techniques that can make your sensitive data end up in the wrong hands. QR codes are just one example of misusage of new technology that is supposed to make your life easier. But don’t worry: this doesn’t mean that all QR codes are up to no good. Just like with every new piece of technology in the market, there will always be a way for it to be used for the wrong reasons.

The Internet as we know it is entering a new phase: Web 3.0. The Internet was born in the 60s when it was meant to connect computer devices to universities across the United States. Only four were initially used, but eventually, many other universities took part in this, and it stretched to Europe. After that, it was known as the Internet. We saw the first promising years of the Internet during the 90s, which was known as web 1.0. It might sound complicated, but it just means that websites were static, and users couldn’t interact with them. Nonetheless, everyone knew that this would be the new way of communicating and gathering information.
It was only a matter of time before people could upload content on the Internet. Blogs, forums, comment sections, report pages, and messaging portals made it possible for people to interact with the websites they grew to love. Web 2.0 gave rise to popularity for modern-day social media, which made it easy for people to upload their own music and videos and stay connected with friends and family from all over the world. While this was an amazing achievement, some downsides were inevitable. It’s easy for anyone to dig up information about anyone publicly online. In this day and age, online privacy is basically non-existent. But the main issue with Web 2.0 is that whenever somebody uploads a piece of content, it does not technically belong to the user anymore.
Web 3.0 is built around blockchain technology, and this will be the new and improved Internet. Blockchain is a publicly accessible domain that shows transparent transactions for any user. This means that if you upload a piece of your artwork, they will know that you are the original creator. Nobody can claim your artwork as theirs. And this goes for anything that can be traded online. This will protect the content creator to the fullest. We’re still in the early stages of this, and it’s only gonna get more interesting. Major corporations are developing metaverses where people can transport themselves into virtual realities.
In this world, you can socialize, buy stuff, and interact with the world around you. You can pick any avatar you want and wear anything you feel like. Hey, you wanna dress up as an astronaut? You can! You can go to different planets across the metaverse and meet all kinds of crazy-looking avatars. In the workplace, you can even attend different meetings with co-workers to discuss work-related stuff while physically sitting at home. Gaming will also be elevated to a brand-new experience where players are immersed in a world where they can be anyone or anything. This will be the future that we will get to witness in the coming years.











