I Will Not Pay My SIL for Babysitting — She’s Living With Us Rent-Free

Analog television never had a channel 37. Land on that channel, and you’d probably just get static. It’s not like missing the 13th floor in a building — channel 37 is an entirely different story. To go on the air, channel 37 would have to transmit from the 610 MHz band. This was the same frequency that the observatory of the University of Illinois needed for radio astronomy. So, if this channel occupied up the 610 MHz frequency somewhere within 600 miles from the observatory, it would have interfered with their giant 400-foot-long telescope, which is one of our windows into the universe. The radius here is huge. It literally envelops all of the East Coast, together with major cities like Detroit, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and St. Louis.
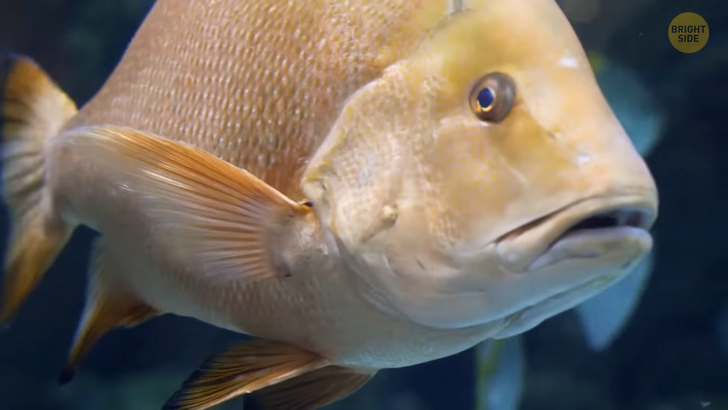

Why fish don’t have necks? Even if you can perform an excellent butterfly or an awesome backstroke, there are still anatomical nuances of the human body that hold us back as swimmers. We need to breathe, our limbs don’t look like paddles, and even having a neck is a “problem.” It’s something that only animals on land need. The neck generally hinders more than it helps when you’re trying to swim faster through the water. So fish never even bothered to develop it in the first place.
Most fish are shaped like torpedoes. This allows them to move forward through the water, driven by their tails. It’s a lateral motion. They move their entire body to a certain degree as they push against the water. Their heads are actually in line with their body through shoulder girdles. With a neck, the fish would be able to rock its head back and forth, which would make its muscles work way harder because it would have to keep looking forward against the lateral motion of its body and tail. There’s a type of fish that’s like the bridge species between the land and the ocean. It has thick fins that could act as crude legs. Its spine included neck joints, which would have allowed this creature to snap its head quickly at prey or peek above the surface of the water.
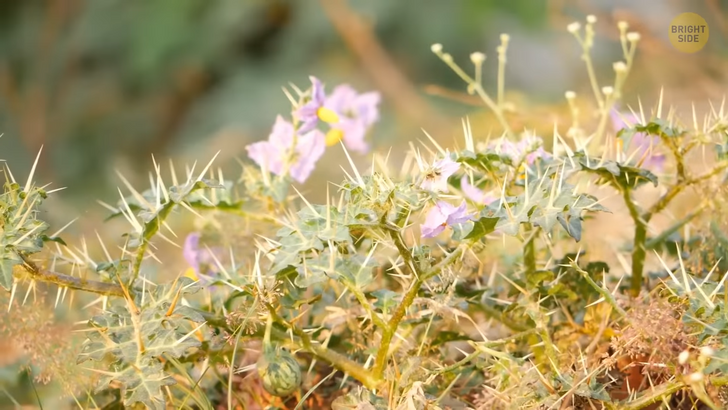

If you’ve ever slid across the lawn when playing soccer or catching a ball, you know how grass can be itchy. It may feel and look soft, but it causes micro-abrasions on our skin. They are invisible to the naked eye, but blades of grass are covered in very small hairs we call trichomes. They make both grass and other plants unappetizing to all kinds of animals, which is how plants actually protect themselves. The tiny cuts we get allow sweat to seep into the tissue, which is literal salt in the wound — that sometimes causes a pretty irritating burning sensation, also known as itching.
You’ve probably noticed that when you’re sick, only one of your nostrils gets blocked. This happens because of what we know as the “nasal cycle.” We’re not quite aware of it, but our bodies direct the airflow more through one nostril than the other on purpose. As we breathe, we switch between nostrils every couple of hours. A constant airflow could dry out the nostrils and damage our lining. Since our body allows one nostril at a time to rest, this doesn’t happen. When you have a cold, the blood vessels in your nose dilate which is a part of how your body protects itself. Also, your nose produces more mucus. Both of these changes lead to stuffiness in your nose, but you’ll feel more blocked in the nostril that’s “off duty” at that time. The nostril with the normal airflow might be fine.
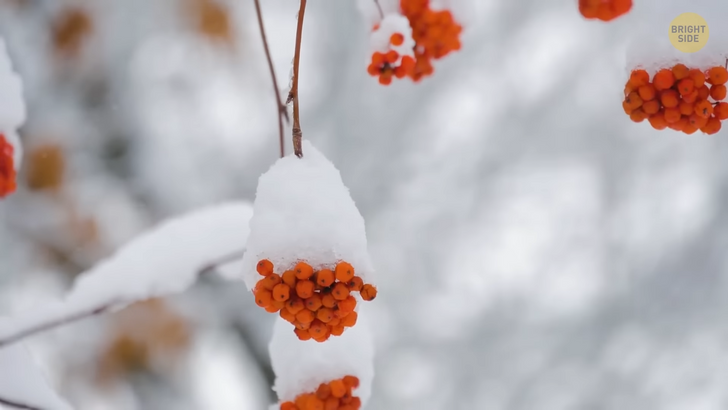

Why is snow white, if ice and liquid water mostly appear clear? H2O is a clear substance, but it can still transform into something white. For example, take a piece of glass, like a windowpane, get a hammer and smash the pane into smaller pieces. Now it looks white. This happens because of the difference in how light interacts with a single surface, like a window versus multi-faceted ones, like the glass you broke. The same thing happens to snow. When light hits an object, it either passes through that object, gets absorbed into the object, or bounces off of the object, which means it gets reflected. When light strikes a smooth flat surface like ice or glass, its visible rays pass straight through it because their paths are not disturbed. And our eyes only see objects in the way they process the light waves absorbed by or reflected off of them, so we mostly see ice and glass as being clear.
But, there are countless uneven surfaces when it comes to shattered glass. When light strikes them, it reflects and goes in all directions. And snowflakes are made up of hundreds of tiny ice crystals in different structures and shapes. The light that strikes snowflakes and shattered glass is reflected back equally, so these rays include all of the wavelength colors of visible light — violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red. And all together, they look white, which is why we see snow like that too.
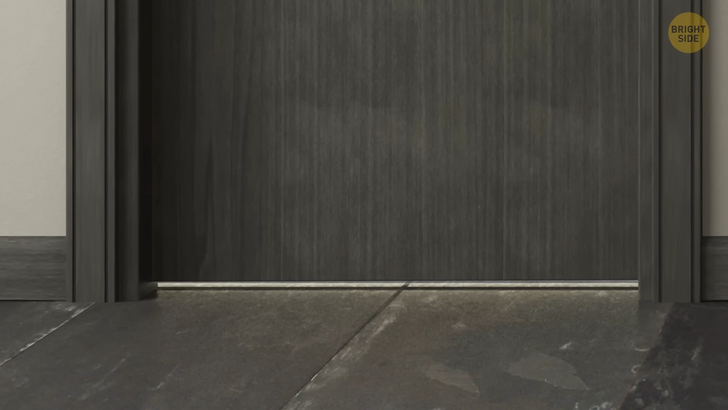

What’s with the gap at the bottom of doors? The space you see there is necessary for airflow when the door is closed. This especially matters in new homes with air conditioning and central heat. No air could flow normally through the ductwork or registers if it wasn’t for the gap. This would largely affect the balance of your cooling and heating system. It would also make staying at your home quite uncomfortable. Also, the gap is there so that the door doesn’t hit stuff on the floor when you open it — like a mat, a rug, or any other loose stuff you haven’t swept up yet.
Why do you feel hungrier when watching TV? Research showed that television isn’t something that stimulates our appetite — it’s more of an appetite distraction. When you watch a movie, you get engaged in the program, so you’re paying less attention to the things around you or things happening inside of you, like your brain telling you you’re full and that you don’t need to eat anymore. Also, when you often combine TV and snacking, it creates a cognitive concept, which means your brain will think it’s always a good idea to do these two actions together. So, you might start reaching for chips or some pizza, not because you’re hungry, but because your brain kinda identifies television with eating. And if the movie you’re watching is longer or you even decide to binge on your favorite TV series, chances are you’re going to eat more.

Why does the sun make your hair lighter? It seems like the sun breathes new life into your hair by making it naturally blonder, but lighter hair during the summer months is a result of the sun damaging your hair. When you’re exposed to sunlight for too long, the melanin in your hair wears down. Melanin is what gives our skin and hair pigmentation. It also protects our delicate DNA from radiation in the way it absorbs and scatters ultraviolet light. But it can’t completely protect us from the harmful effects of the sun. After you spend enough time in the sun, it begins to break down. And hair then loses pigmentation so it becomes lighter.
Why is it better to not drink anything than to drink seawater? The main element in salt is sodium, and it’s generally good for us because it’s an important electrolyte that helps with regulating blood volume and some other bodily functions. And our kidneys get rid of the extra salt that our body doesn’t need. That’s why, when we eat a giant bag of chips, we might feel insanely thirsty. It’s just our brain telling us to drink water so our kidneys can get rid of the extra salt. Our body can’t process seawater because the salt concentration, which is called salinity, is too high — 4 times the salinity of our blood. So if we drink saltwater, our body will shift the water we need inside our cells to the blood. And this will affect our brain functions pretty quickly and lead to worse scenarios.
Light represents the maximum speed at which information can go from place to place. Nothing can match the 186,000 mps light achieves when traveling through a vacuum, not even sound. That’s why you see lightning before hearing thunder. Sound consists of waves of compression and expansion in a substance and since nothing exists in a vacuum, neither does sound. In a normal scenario, it moves through the air at 0.2 miles per second. Light is slowed down when it’s passing through transparent materials — by approximately 33 percent when it’s zooming through glass. But it still passes through glass nearly 50,000 times faster than sound waves. If we could increase the speed of sound, thunder would be way scarier. Sound waves are composed of tiny pieces where each moves just enough to collide with the one it’s closest to. That creates areas of lower and higher density within the wave. Imagine you have humid air during a lightning storm. The sound wave here comes through and squeezes stuff pretty hard. Then it expands out which makes the pressure drop. This would cause the humid air to freeze, so we’d be able to see a lightning bolt through a pretty dense fog of ice crystals.











