My Parents Refused to Fund My Education, So I Turned the Tables on Them


In today’s fast-paced lifestyle, many of us find ourselves rushing through meals without thinking twice. But health experts warn that eating too quickly can come with several unexpected downsides. Here are 7 potential consequences of eating too fast — and the science behind them.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE. SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
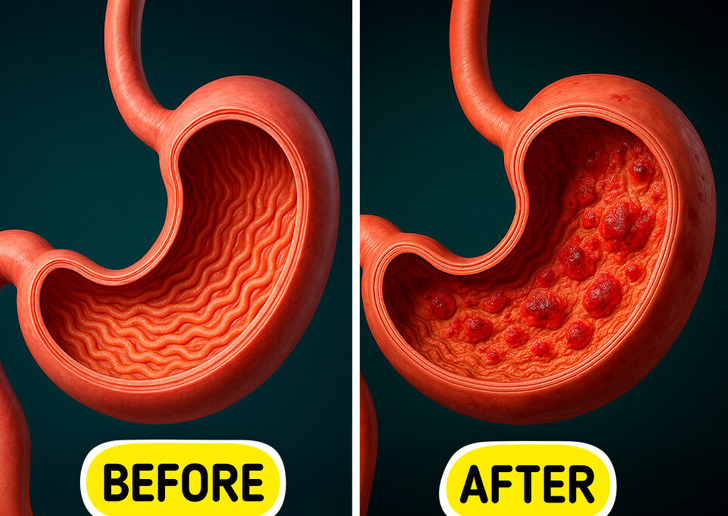

Eating too fast can cause a bloated stomach because it leads to swallowing more air, which increases the amount of air trapped in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in bloating and discomfort. Additionally, the types of foods often consumed quickly—such as fast food items like burgers, nuggets, fries, and sugary beverages—can have other negative effects on health.
While it’s easy to rush through meals, slowing down can lead to big health benefits. From better digestion to reduced risk of chronic diseases, mindful eating is a simple habit that can make a lasting impact. So next time you sit down to eat, take a deep breath—and take your time. More articles about your health can be found here.











