20 Dogs That Forgot They Were Dogs and They Don’t Really Care


Opossums are one of the few animals who have opposable thumbs on their paws, just like humans. This helps them grab and grip things so it’s easier for them to climb. Moreover, their little paws also have friction ridges that are similar to our fingerprints.
While a tickled rat’s giggles cannot be heard by human ears, special microphones allowed scientists to listen to their squeaks. Rats are most ticklish on their backs and stomachs, but they have to be in a good mood to enjoy it. The rodents would even chase the researchers’ hands for more fun after they stopped tickling them.
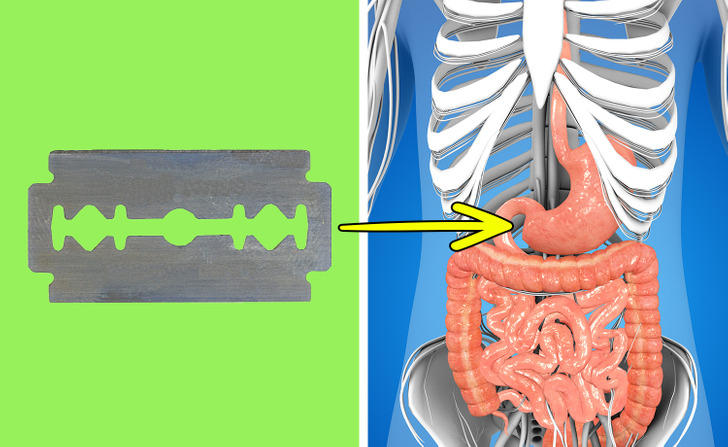
The fluid in our stomachs is so acidic that it can break down razor blades. In 24 hours, most razor blades become so fragile, they start to dissolve. The experiment was simulated in a laboratory using gastric juice, so we definitely shouldn’t try this at home.
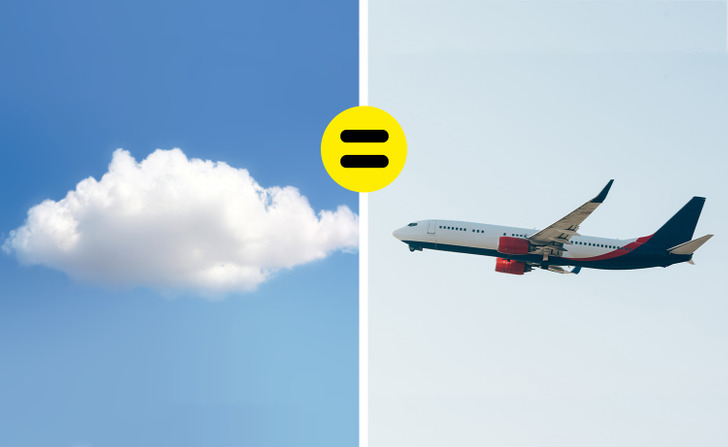

While they look fluffy and light, clouds can actually weigh as much as the heaviest airplanes, which is around 1 million pounds. But don’t worry, the mass of a cloud is evenly spread out over a huge surface and the air below it has a bigger density. So that’s how they can still float in the sky.
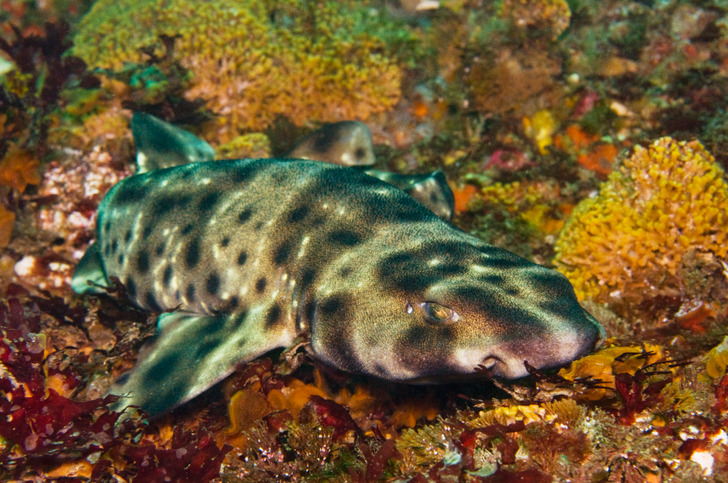

Scientists have discovered that there are a few species of sharks that glow in the dark. One of these species, called the kitefin shark, is nearly 6 feet long. The cells of these sharks produce a soft blue-green light in the dark.
Butterflies use the sensors on their feet to get information about the plants or flowers they land on. Tasting the plants allows the butterflies to decide whether they are edible or not.
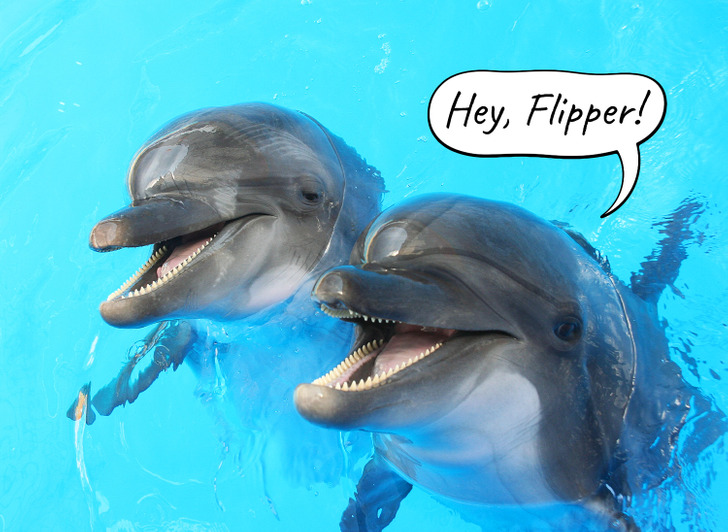

Dolphins are definitely smart creatures. They even use special whistles to identify each other. Dolphins use these signature sounds the same way humans use names to communicate.
While during the summer reindeer have a golden brown pair of eyes, in the winter, they turn dark blue. The blue eyes allow reindeer to see better in the darker months.
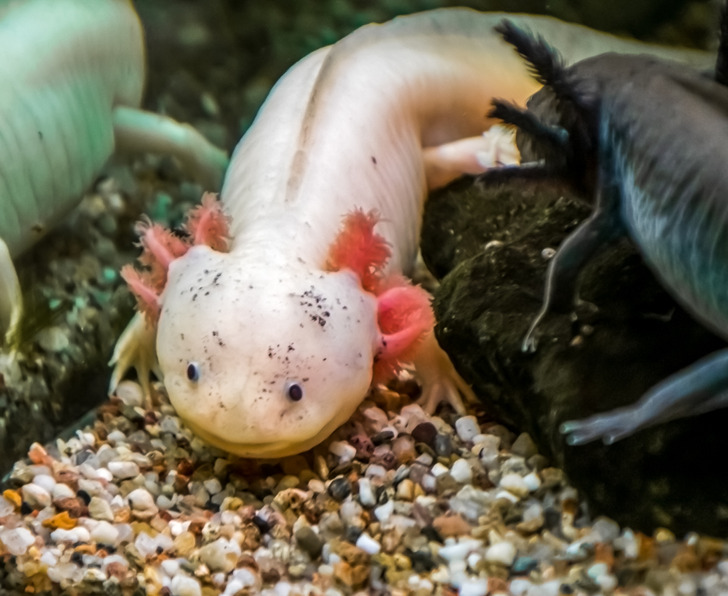

Axolotl, a Mexican species of salamander, can regenerate missing limbs, tails, and even parts of their brain and heart. They can even make brand new connections in their brain to allow them to use paralyzed limbs again.
While humans can convey 27 emotions, horses are capable of making 17 distinct facial expressions. Horses too can use their facial muscles and features to alter their expressions and communicate.
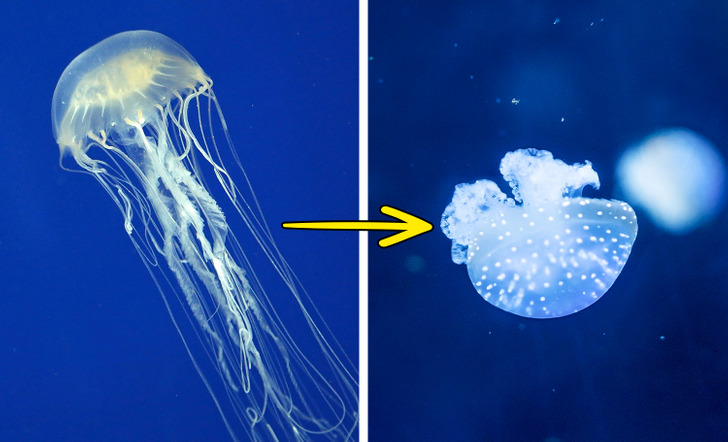
The immortal jellyfish species is able to reverse its own aging process and revert to a younger life cycle. This process allows the jellyfish to repeat the cycle without a limit, so the species never has to die, unlike all the other ones.

Sea lions are actually very musical creatures, and they can keep the beat for some time. Scientists made the discovery while studying a sea lion nicknamed Ronan. Ronan can bob her head to the musical rhythm and can even dance to songs researchers play for her.
Male foxes choose their partners for life and stay loyal during and even after their relationship. They won’t look for a new partner even after the female fox’s death. However, vixens have different habits, as they will seek out a new mate as soon as their current one dies.