I Refuse to Keep Visiting My Husband’s Family—I’m the Breadwinner, Not Him

Most people think only diabetics have high blood sugar levels. Yet this isn’t so. Any person can suffer from this and may not notice the harm being done to nerves, blood vessels, and organs.
We at Bright Side are sure that in order to prevent complications, it’s important to recognize worrying symptoms in time and take appropriate measures.
High blood sugar prevents glucose from entering cells. As a result, the body doesn’t receive energy and asks for food again and again: it’s a vicious circle.
At a high blood sugar level, the body is unable to store and absorb glucose properly. Energy is used inefficiently, and body cells don’t receive the fuel they need. All this leads to the fact that a person often feels tired for no reason.
If the blood sugar is too high, the kidneys cannot reabsorb fluid. Therefore, the body, trying to equalize the glucose concentration in the blood and in the cells, dissolves blood with intracellular fluid, thus bringing the concentration of glucose to normal. This results in frequent urination.
A dry mouth and strong thirst are responses to severe fluid loss. The hypothalamus, which assesses the level of dehydration and causes thirst, sends a corresponding signal to the brain. Of course, you cannot refuse to drink, but it’s better if you choose water or tea without sugar.
With a high glucose level, you can lose weight within a short period of time, even if meals are frequent and contain a lot of calories. There are several reasons for this:
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and yeast infections can occur in both men and women. Yet much more often they’re found in women with high sugar levels and diabetes. A large amount of sugar creates a favorable environment for the reproduction of yeasts and bacteria.
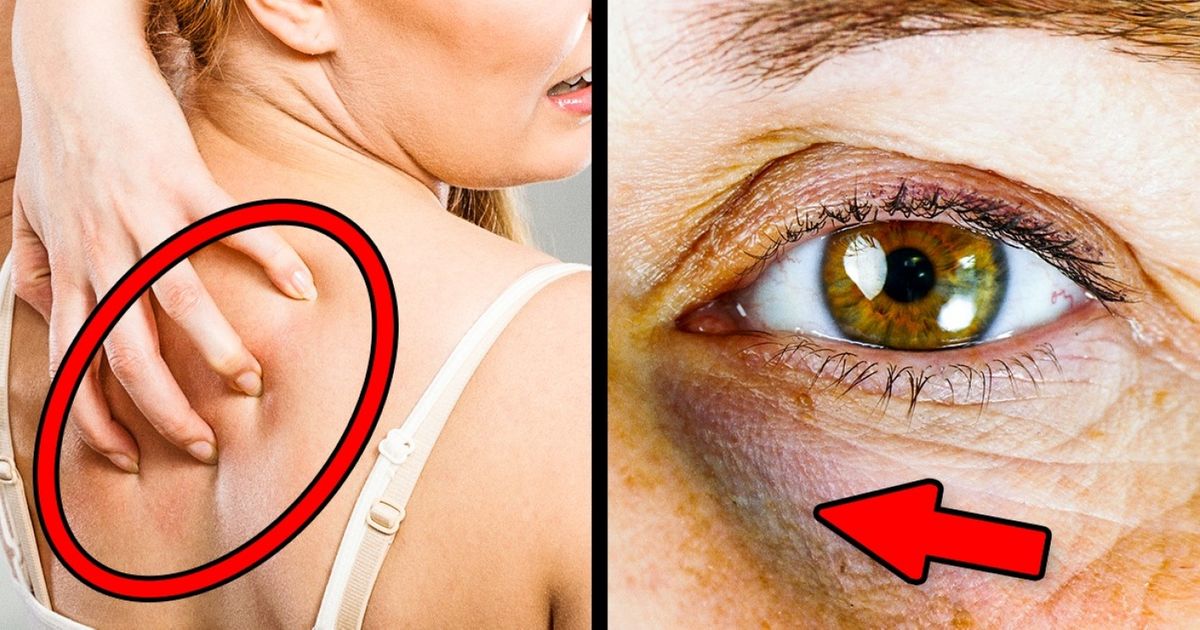
Dry skin may be connected with high blood sugar levels for various reasons:
High sugar levels prevent glucose from entering the brain cells, so the brain experiences difficulties obtaining energy. This adversely affects the speed of thinking and decision-making.
Blurred vision is also the result of a dehydrating effect due to high blood sugar — it also affects the cells of the eye. As a result, they deform and the eye loses its ability to focus properly.
This happens due to vascular damage as a result of high sugar levels. This leads to a worsening of blood circulation, especially in limbs, and insufficient nutrition of tissues.
According to research, people with high sugar are more anxious, irritable, and tend to depression.
The brain depends on an equal supply of glucose, and sharp jumps of its level negatively affect its work. As a result, our mood suddenly gets worse.
Sugar also affects the absorption of another nutrient responsible for mood: chromium. This mineral is needed to maintain a stable level of blood sugar because insulin, which cleans glucose from the blood, cannot work properly without it.











