Meg Ryan’s Fans Are Glad That the «Damage Wasn’t Permanent» as She’s Finally Looking Like a 62 Y.O.

Gluten may seem harmless, but for some, it can quietly trigger serious health issues. Without obvious warning signs, its effects can go unnoticed, leading to lasting damage over time. Understanding your body’s response to gluten is essential for protecting your health.

The symptoms primarily affect the intestines and include nausea, bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and even constipation. These signs are often mistaken for other conditions, leading many patients to be incorrectly diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome. Research shows that 10-15% of the global population suffers from IBS. However, for individuals with gluten sensitivity, this misdiagnosis can prevent them from receiving the proper treatment, leaving their symptoms unresolved.
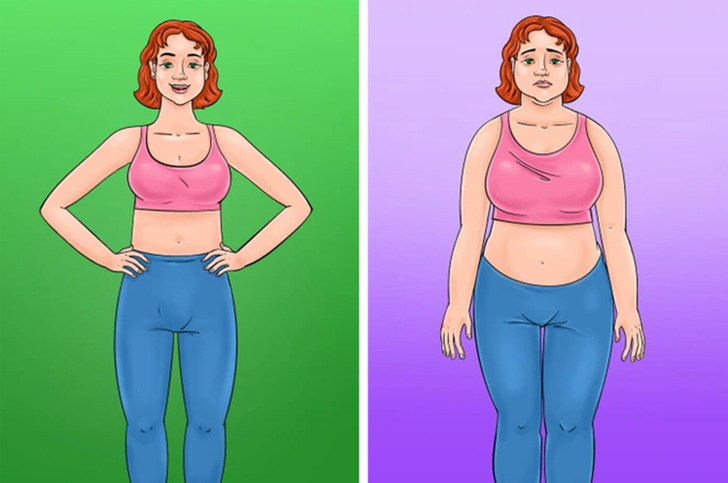

Gluten intolerance can cause unexpected weight fluctuations, leading to either weight loss or weight gain without a clear explanation. This occurs due to inflammation at the cellular level and disruptions in metabolism. While sudden changes in weight might indicate various health issues, they could point to gluten intolerance if paired with other symptoms of malabsorption.
Gluten intolerance is closely linked to hormonal imbalances, manifesting as irregular menstrual cycles, unexpected weight changes, PMS, and sleep disturbances. These hormonal disruptions can become more pronounced during significant life stages such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Notably, these symptoms are predominantly observed in women.
Gluten contributes to increased inflammation and intestinal permeability, leading to a range of neurological and psychological symptoms. These may include difficulty concentrating, depression, anxiety, insomnia, fatigue, irritability, and “brain fog,” where individuals struggle to maintain focus or clarity of thought.
Research also indicates that people with gluten intolerance are more likely to experience migraines compared to others. While headaches can stem from various causes, those with gluten sensitivity may notice a headache occurring 30-60 minutes after consuming gluten-containing foods.
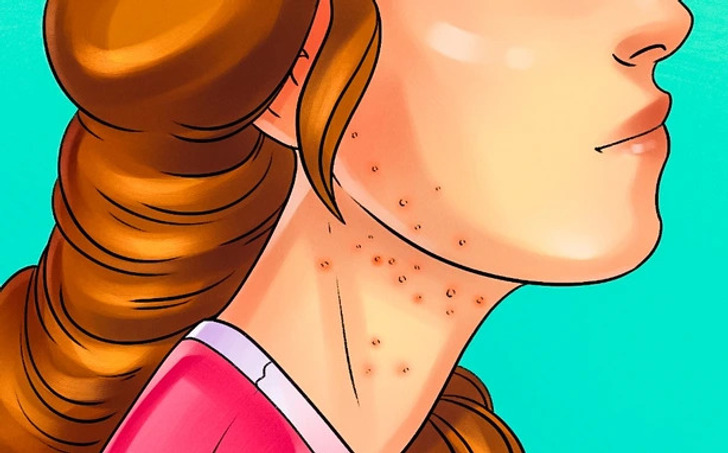

Gluten intolerance is closely linked to certain skin conditions, including keratosis pilaris and herpetiform dermatitis. Symptoms often manifest as itchy rashes that may appear on the hands, torso, face, buttocks, elbows, or along the hairline. Additionally, gluten sensitivity can lead to weakened, brittle nails and other skin irritations resembling eczema, which may result from gluten-induced blockages in the body.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is another condition that may be linked to gluten intolerance. This disorder, which affects both children and adults, is characterized by a short attention span and difficulties with self-control. Emerging evidence suggests that adopting a gluten-free diet may help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with ADHD.
Gluten intolerance can disrupt the absorption of essential nutrients and minerals in the intestine, including calcium. This deficiency can lead to various dental and oral health issues, such as enamel hypersensitivity, tooth decay, cavities, and mouth ulcers. If you maintain good oral hygiene but continue to experience these problems, gluten consumption might be the underlying cause.
Celiac disease is frequently diagnosed due to iron deficiency anemia, a condition where the body lacks sufficient iron. Symptoms of this anemia include fatigue, shortness of breath, headaches, pale skin and mucous membranes, and even arthritis. This occurs because gluten intolerance impairs the intestine’s ability to properly absorb iron, leading to deficiencies despite dietary intake.
Many individuals with autoimmune diseases have a history of gluten intolerance. Celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder, occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the cells of the intestine upon gluten ingestion. The challenge is compounded by the fact that celiac disease can increase the risk of developing other autoimmune conditions, including autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune liver disease, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, vitiligo, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
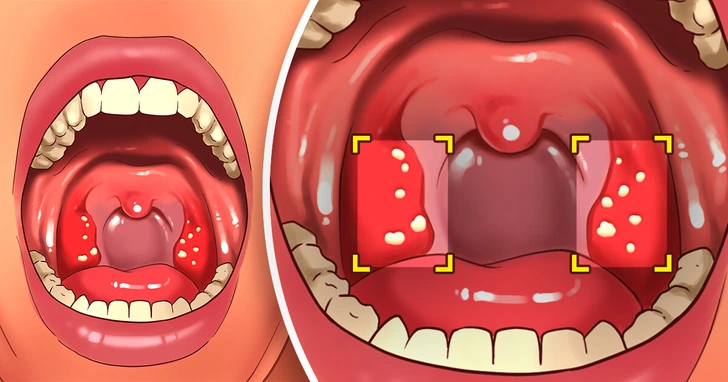
Although not extensively studied, in my clinical experience, tonsil stones are frequently observed in individuals with gluten sensitivity. Many patients report that their tonsil stones often resolve after adopting a gluten-free diet, suggesting a potential link between the two.
1. Get Tested: Visit your doctor for a blood test to check for antibodies typically found in the blood of individuals with Celiac disease. To ensure accurate results, it is important to include gluten in your diet before the test.
2. Remove Gluten from Your Diet: Avoid foods containing gluten, such as:
Always read product labels carefully, and opt for foods marked as “gluten-free” when possible.
Read more useful articles about health and wellness here.
8 Dermatologist’s Tips for Radiant Skin in Cold Weather











