16 Stories of Mother-in-Law Kindness That Restored People’s Faith in Family


Hey, can you speak up? I just ate an entire pizza! That’s because after eating a hearty meal, our hearing tends to be a bit less sharp. During digestion, most of our bloodstream is directed toward the stomach, which takes away a bit from all the other organs. So next time you want to go listen to your favorite band at a live concert, make sure to eat a lighter meal to keep your ears pitch perfect.
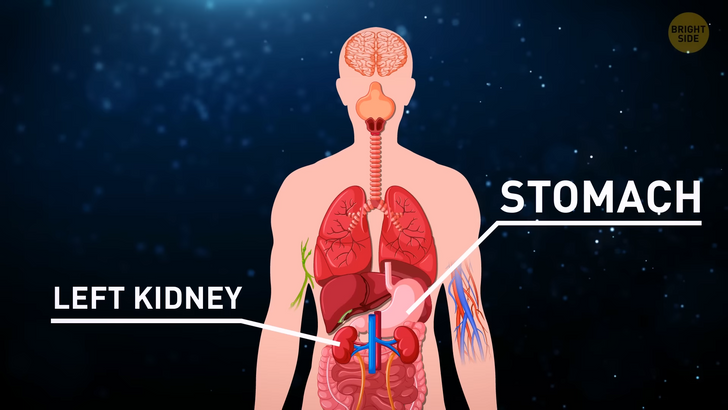
On top of our stomach and left kidney, we have a magical organ that can grow back if we remove a part of it. Our liver can regenerate itself by making new cells called hepatocytes. They begin to multiply once the liver is damaged. The seriousness of that damage defines if it can regenerate completely and the amount of time it takes to do so.
Ever wondered what’s worse for your body: no sleep or no food? Turns out, the lack of sleep is more dangerous. That’s because if you don’t rest, your body becomes exposed to a lot more risks. After 24 hours without any shuteye, you can start to have memory problems and find it difficult to concentrate. At just 17 hours without sleep, you start to feel tired and groggy, irritable, tense, and more emotional! I need a nap. Your pain receptors also become more sensitive, which means everything hurts a bit more than it should. Oh, and it affects your hearing, too. What? On the other hand, you can be well into your 24-hour period with no food before your body realizes you’ve stopped eating. In the first eight hours, you just keep digesting the last meals you had. After those first hours, you start to use stored fats for energy. Not eating for more than 24 hours means that your body will start “eating away” at its own protein, which means you literally start to lose muscle.

Rainwater isn’t always safe to drink. It can sometimes hold harmful bacteria and viruses. Also, in heavily polluted locations, it may even meet other harmful materials. Some communities out there do depend solely on rainwater as their primary source of hydration. But does rainwater have any other health benefits? Not really, based on current studies. Some of those risky substances may be removed from rainwater if you boil it, but it’s best to stick to the safer side and only drink water from sources that are 100% safe for human consumption.
We produce sweat mostly to regulate our body temperature and for some added moisture — like the one we need in the palms of our hands for a better grip. But sweat doesn’t just show up on our skin. It comes out of around five million pores in our bodies.
We’re literally stepping on a quarter of our bones each day! We have just over two hundred bones in our bodies, but about a quarter of those are in a very small, surprising area: our feet! Since we have twenty-six bones in each foot, we end up with fifty-two in both.
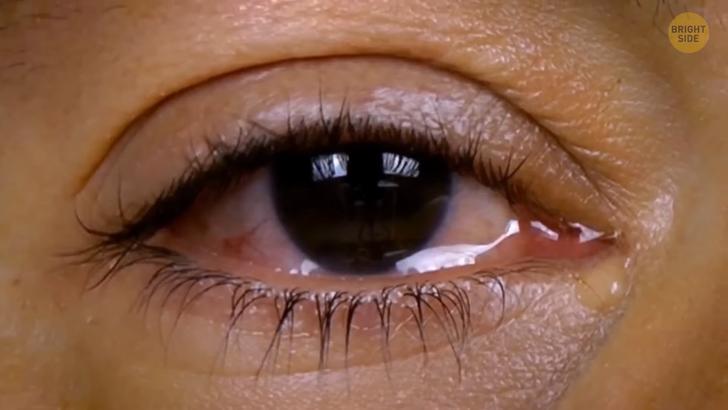

Our eyes produce tears for many reasons, like protecting themselves from infections or clearing up debris, such as smoke and dust. Or when your baby has done you wrong. But the number of tears we produce is quite surprising: up to thirty gallons per year! That’s almost enough to fill a bathtub! Wow, that is heartbreaking!
Our blood pressure “wakes up” hours before we do. That’s because, in the morning, the body produces a bunch of hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline. They help give us the energy boosts we need during our morning hours, but they also increase our blood pressure — which is usually higher between 6 am and noon. During the night, since we should technically sleep and perform no physical activity, our blood pressure drops by up to 20%.
Speaking of our vital fluid, our blood accounts for about 10% of our total body weight. We tend to think of our body weight as being mostly made up of muscles, fat stores, and bones, but there’s a lot more to it. In a fit adult person, bones make up 15% of the total body weight. About 40 to 45% is left to muscles, about 15% to fat deposits, and the rest are stuff like skin, tendons, hair, and other lucky things. Let’s see, that adds up to ...yep, 100%.
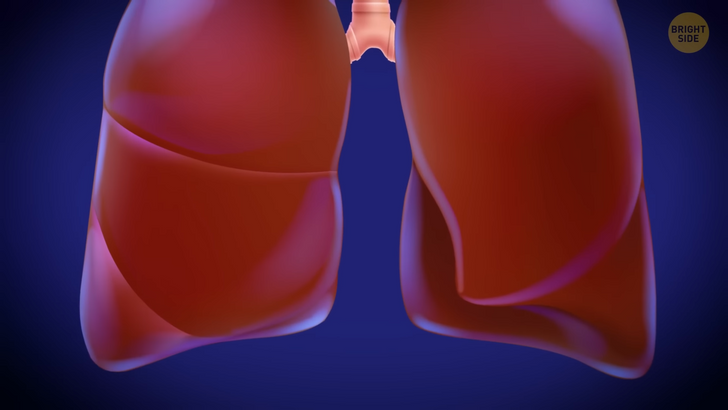
Your lungs aren’t twins; they are siblings! That’s because they aren’t the same size or shape. Your right lung is bigger and tends to weigh more. And your heart is to blame for it since your ticker tilts to the left a bit. This creates a small indentation in the left lung — called the “cardiac impression”, which is also what funny heart doctors do at comedy clubs. The right lung may be bigger, but it’s a bit shorter since it needs to make room for the liver. Doesn’t your house have a liver room?
Many of your body measurements are quite symmetrical in surprising ways. If you were to stretch out both of your arms — your “wingspan” — and measure it, it should show how tall you are. Based on these similar measurements, specialists can even produce theories about what ancient humans used to look like. Looks like we’ve evolved to be increasingly symmetrical to appear more attractive and healthier to attract mates. Hmm. More so, since we’ve evolved to also walk on two legs, our symmetrical features help us to move around with the least amount of energy because it creates balance.
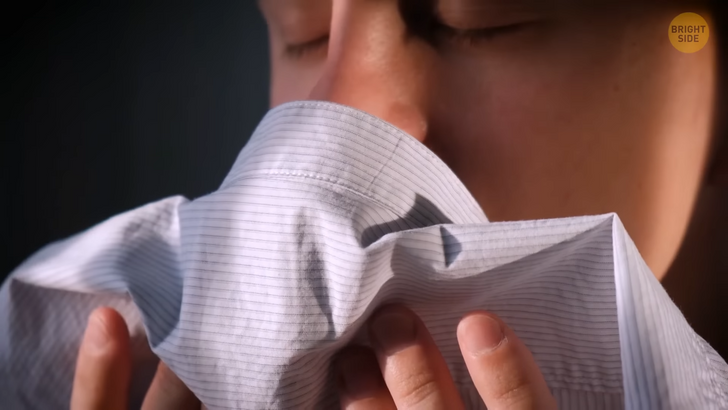
Humans aren’t natural champions when it comes to the scent of smell, that’s for sure, but our noses can pick up about one trillion different scents! Scientists are still performing research on this subject and believe the number may be even higher. Some dog breeds may be able to notice scents somewhere between 10,000 to 100,000 times better than we do but turns out the best nose in the animal kingdom may be attributed to the elephant because of its staggering number and type of olfactory receptor genes: over 10,000 — while humans and chimpanzees have less than four hundred.
We tend to look at our pinkies as our most delicate fingers, but we do have more power in them than we think. Turns out that should our pinkie finger be lost or affected; the overall strength of our grip may decrease by up to 33%.
The liquid in our stomach is way more powerful than any acidic food you can think of — like lemons, pineapples, or tomatoes. The pH of healthy stomach acid should be between 1 to 3. So, if you think about it, it’s just below that of battery acid!

Our hair strands are strong, too — so strong that research is performed on them to duplicate their resistance onto human-made materials. A healthy head of hair should be able to withstand up to 26,000 pounds! It’s due to a little protein in the hair strands called keratin — which you can also find in your nails and skin.
Only about one-third of us humans have perfect vision. There are a lot more glasses and contacts out there than you’d think, making up about 66%. Apart from different eye conditions, our vision also gets worse with age.
When we’re born, our heads amount to one-quarter of our total length. By the time we reach twenty-five, our head will only be one-eighth of it. That’s because our heads won’t change their size a lot as we grow older, as opposed to the rest of our body, mostly when it comes to the legs and torso.

Our brains are these super-powerful computers, and a single human brain cell can hold five times as much information as the entire Encyclopedia Britannica! Maybe you remember that. We’ve yet to pinpoint the exact amount of data it can support, but in electronic terms, the storage capacity of the brain is around 2,500 terabytes. For comparison, The National Archives of Britain, which keeps over nine hundred years of history, only takes up seventy terabytes. That’s probably the reason our brains need the most amount of oxygen compared to other organs: about 20% of the total oxygen that enters the bloodstream. And that’s despite the fact it makes up only 2% of our body mass.
Our normal activities, plus the effect of gravity, make the cartilage in our ankles, knees, hips, back, and neck slowly compress. Once you rest overnight, the cartilage goes back to normal. On average, you are somewhere around 0.4 inches taller in the morning than you are later at night. And that’s why they call me “Stretch”.











