people also seem to be more attuned to nonsense-like a brain overload!!!
How Humans Have Evolved in Just 150 Years and 7 Big Changes in Our Bodies

The origin and evolution of the human species are taught in classrooms as an event that took place thousands of years ago. The study of this process is addressed as if it belonged to history and not precisely as a biological question. We think that hominization, or human evolution, ended with our ancestors, the Homo rhodesiensis, and we ignore the fact that the human body of today has also undergone adjustments in recent years.
Bright Side will show you the evolution of the contemporary human body.
1. An increase in height

There’s evidence that human height has risen over the past 200 years. A study from the scientific journal eLife showed that both men and women were seen to have height increases in various countries around the world, especially South Korean women and Iranian men, who became 20.2 cm and 16.5 cm taller on average.
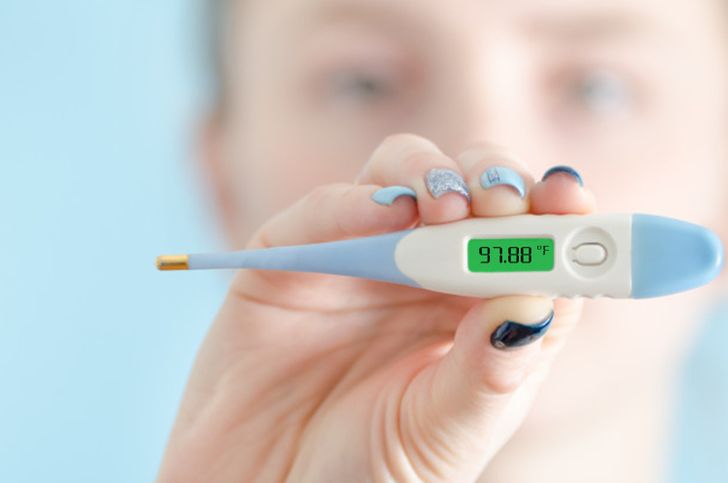
2. Body temperature
While the planet’s temperature is on the increase, human body temperature is on a decline. Researchers from Stanford University have confirmed that men from the 21st century have decreased their body temperature by 1.06ºF, in comparison with data from the 19th century. Data from the 1800s shows that women have also experienced a decrease of .58ºF.
3. Early puberty
Boys and girls reach adolescence earlier than children from a century ago. This is due to good nutrition and health. According to a study from the University of California, 15% of girls start puberty at 7 years old. Puberty is estimated to be one to 2 years ahead of what early 20th century records state.
4. Longevity
The life expectancy of the human body has increased because of advancements in sanitation, nutrition, hygiene, and other factors. A report, published by the Santalucía Institute in Spain, predicts that longevity will continue to rise until it reaches 120 years by the end of the 21st century. If we compare data from the beginning of the 20th century, in which only 26.2% of the population survived to age 65, we can say that many millennials will become supercentenarians.
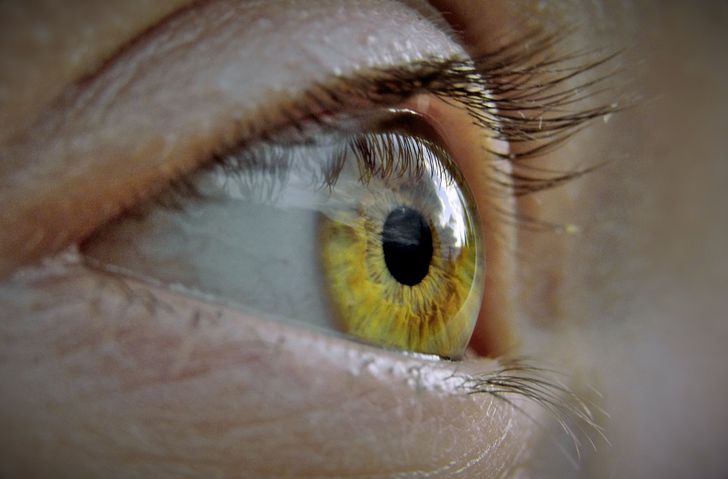
5. New parts and organs in the human body
Thanks to the development of science and technology, recent studies have reported previously unknown body parts, among them is the interstitium. This organ, which has generated much controversy among scholars, is a network of cavities made out of collagen and elastin in all body tissues. In 2013, a sixth ocular layer was also discovered in eyes. It’s called the Dua’s layer and it is only 0.04 inches thick.
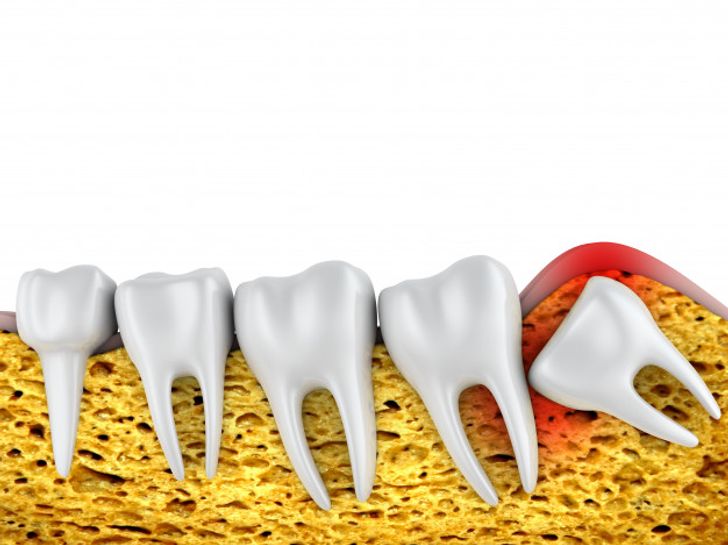
6. Body parts that have disappeared or will disappear
In connection with the previous point, other parts of the human body will definitely disappear in a few years. Some people are already being born without wisdom teeth, also known as third molars. This is because of the decrease in the size of our jaws, resulting from our change in diet. Another example is the palmaris longus muscle, which runs from the elbow to the wrist. Several people have already been born without it because it was fundamentally used for climbing.
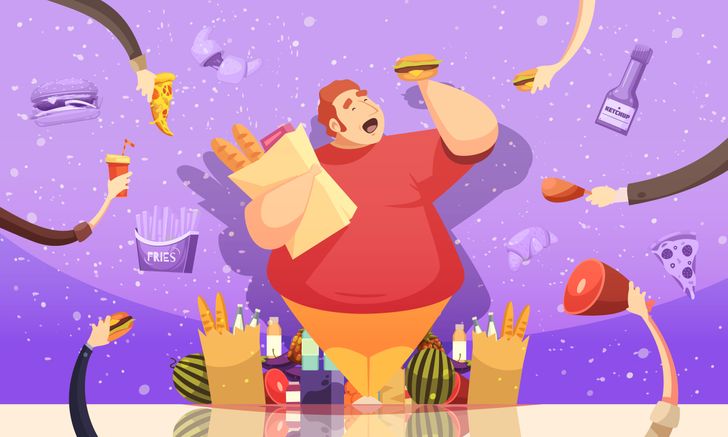
7. Obesity
It’s no wonder why we’re less robust, we now have lots of junk food. According to the World Health Organization, obesity has almost tripled since 1975. Data from 2016 showed that more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, and among them, more than 650 million were obese. Experts have pointed out that changes in eating habits and physical activity are a result of the lack of support and value seen in fields such as health, education, urban planning, the environment, transportation, and others.
Do you know of other current changes in the human body? Share them in the comments!
Comments
Related Reads
11 Riddles That Toasted Our Brain Like a Marshmallow

Which Girl Will Be Most Attractive When They Turn Around? Learn What Your Choice May Say About You

17 People That Changed So Much They Can Barely Recognize Themselves in the Mirror

11 Spot-On Comics About How Our Life Changes After 25

A Color Test That Can Tell Your Mental Age

20 People Who Have Opened a Portal to a New World With Their Discoveries
12 Stories That Capture the Sweet and Sour Memories of Blended Families

I Refused to Talk to My Parents After They Chose My Ex-Wife Over Me

I Refused to Pay for Our Valentine’s Dinner—Then I Learned the Heartbreaking Truth

I Gave Up My 2-Month-Old Baby for Adoption Because I Chose My Own Happiness

14 Stories From Cleaners That Are Wilder Than Any Movie Script

My Family Excluded My Girlfriend From Christmas Because We’re Not Married