“Aged Suddenly,” Angelina Jolie Surprises People With Drastic New Look

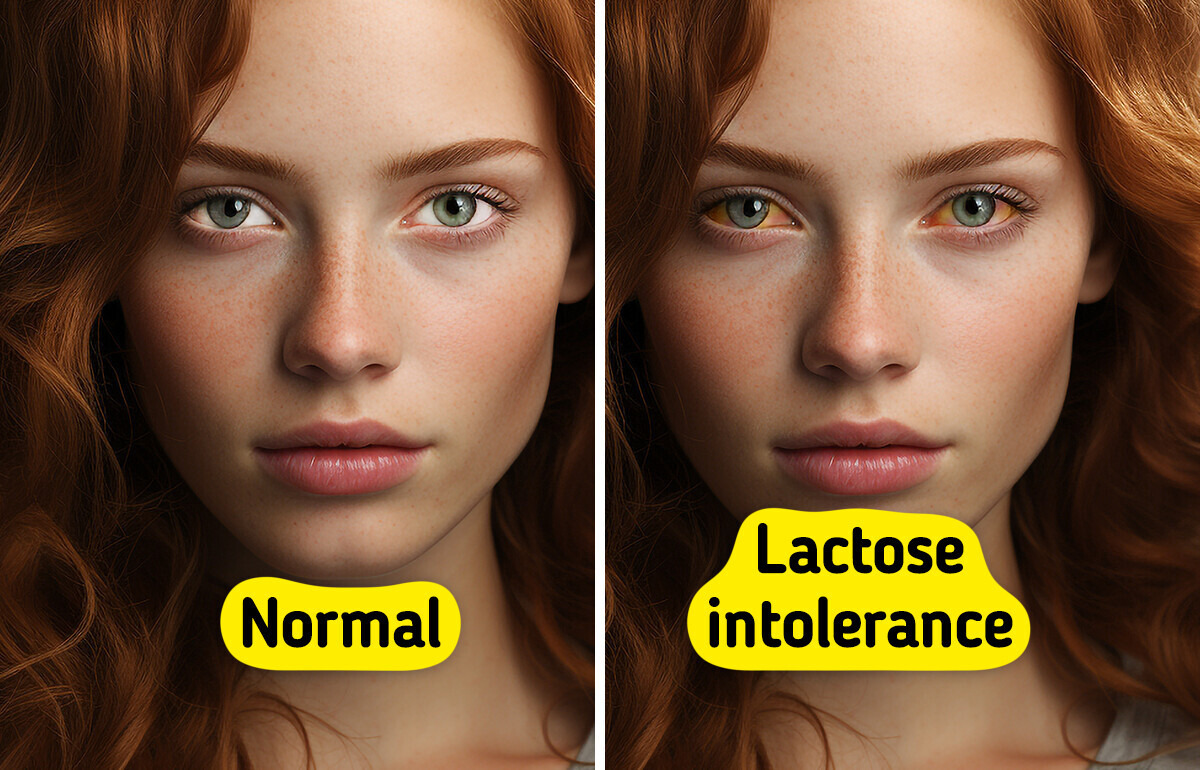
Millions of people experience lactose intolerance, often without realizing it. This article highlights 10 common signs your body may be using to signal that lactose could be the cause of your discomfort.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE.
SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.

Common lactose intolerance can also impact the immune system, triggering increased inflammation in the body. Just like a swollen ankle after an injury, puffy eyes and pronounced under-eye bags may be signs of your body's inflammatory response to lactose.
While less common, some people with lactose intolerance report symptoms like headaches, fatigue, difficulty focusing, muscle and joint pain, mouth ulcers, urinary issues, and even eczema.
Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt have also been linked to canker sores. Some experts suggest that proteins in cow’s milk may trigger mouth ulcers in certain individuals due to an immune reaction.
If you frequently experience mouth sores, consider cutting out dairy, especially from animal milk, and opt for alternatives like soy milk, oat milk, or vegan cheese to see if it helps reduce flare-ups.

Dairy allergies can trigger reactions beyond digestion, affecting the skin, lungs, and more. Common symptoms include:
In babies, blood in the stool can also be a sign of dairy allergy.
More severe reactions, like throat swelling and trouble breathing, may indicate anaphylaxis—a life-threatening allergic reaction. Symptoms usually appear within minutes but can sometimes take hours.
Lactose intolerance occurs when the body has difficulty breaking down lactose, the natural sugar found in milk. This can lead to digestive issues such as diarrhea after consuming dairy products. While the condition, also known as lactose malabsorption, is not typically harmful, it can cause significant discomfort.
Interestingly, lactose intolerance doesn't always result in diarrhea. For some individuals, particularly those whose gut bacteria produce methane instead of hydrogen, constipation can be a prominent symptom. Research suggests that methane production in the digestive system slows down intestinal movement, leading to constipation in about one-third of those affected by lactose intolerance.
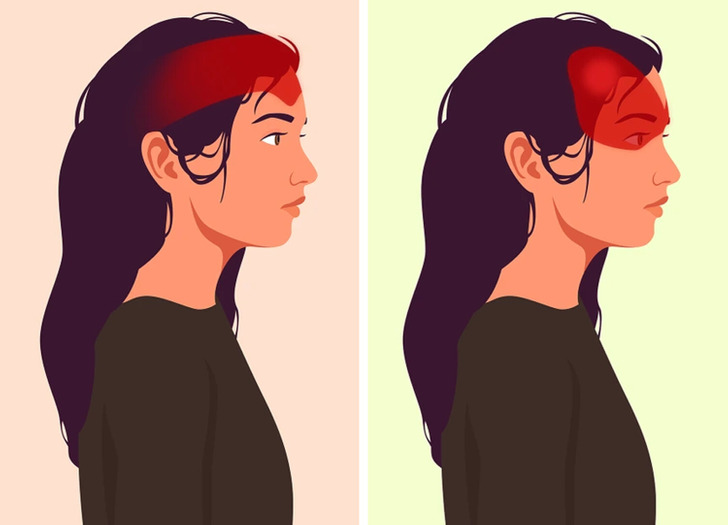

Lactose intolerance can cause symptoms beyond digestive discomfort, including back pain, headaches, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and general tiredness. Some individuals also report sleep disturbances, dizziness, and an overall sense of malaise.
These less common symptoms may stem from the body's inability to process lactose, potentially triggering inflammatory or metabolic responses in sensitive individuals.
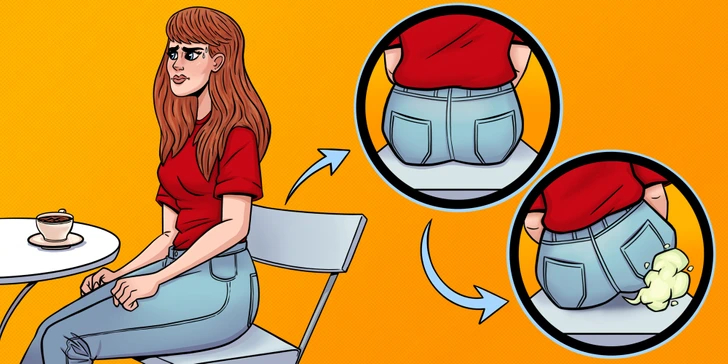
When lactose is not properly digested in the small intestine, it moves to the colon, where gut bacteria break it down.
This fermentation process produces acids and gases like hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide, leading to common symptoms of lactose intolerance, including flatulence and bloating.
Muscle and joint pain may be linked to lactose, the sugar in dairy products. Normally, lactose is broken down by lactase, an enzyme in the small intestine. However, most people experience a decline in lactase production after infancy, making digestion more difficult.
Even for those who can process lactose, it quickly converts to glucose, which can disrupt the gut microbiome, raise blood sugar levels, and trigger systemic inflammation. Whether due to poor digestion or metabolic effects, lactose can contribute to inflammation and pain—something many aim to avoid.
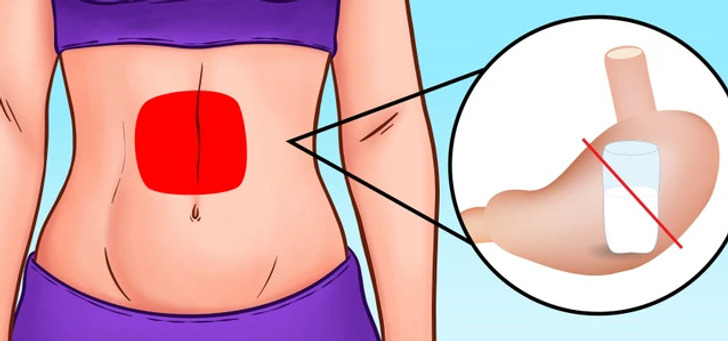
The most common symptoms of lactose intolerance include abdominal cramps and pain, typically appearing within a few hours after consuming dairy products.
If you're experiencing lactose intolerance symptoms, it may be helpful to consider whether gluten intolerance could also be a contributing factor.
12 Ways Your Body May Be Telling You That You Have Gluten Sensitivity











