15 Infuriating Things People Say When They Find Out You Have a Certain Job
A stroke can happen suddenly, but early warning signs often appear first. Recognizing these symptoms quickly can make all the difference in getting the right treatment and improving recovery. Learn what to watch for and how to act fast when every second matters.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL ADVICE. SEEK THE GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
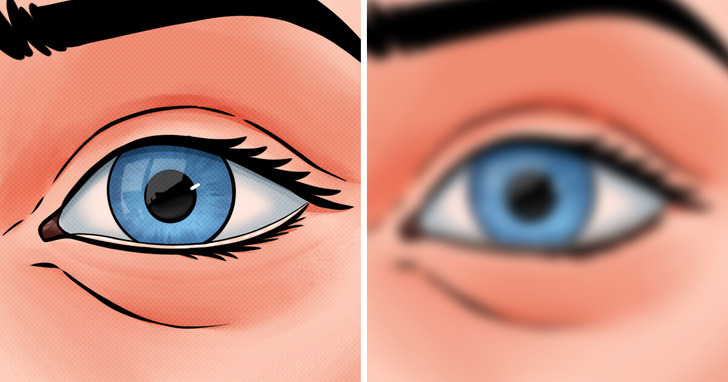
Vision problems are common because the brain processes what we see through a network called the visual pathway. If a stroke damages parts of this pathway or the brain areas responsible for interpreting visual information, it can affect eyesight. Some common vision issues after a stroke include visual field loss, trouble with eye movement, and difficulties processing what you see.
Stroke-related vision problems can cause symptoms such as blurry vision, double vision, difficulty reading, and sensitivity to light. Some people may also struggle with depth perception, recognizing objects or faces, or even experience visual hallucinations.
If you notice any changes in your vision after a stroke, it’s important to see a doctor. They can assess your condition and recommend treatment or rehabilitation to help manage these issues. Getting medical advice early can make a big difference in adjusting to vision changes and improving your quality of life.

About one-third of survivors have trouble speaking, reading, writing, or understanding others. This happens because different parts of the brain control communication, and if a stroke damages one of these areas, it can cause problems.
Aphasia makes it hard to speak, understand, read, or write. It affects everyone differently. Dysarthria happens when weak muscles in the face, mouth, or throat make speech slurred, slow, or quiet. Apraxia of speech makes it difficult to move mouth muscles in the right order for clear speech.
If you or someone you know is having trouble communicating after a stroke, talk to a doctor for help and treatment options.
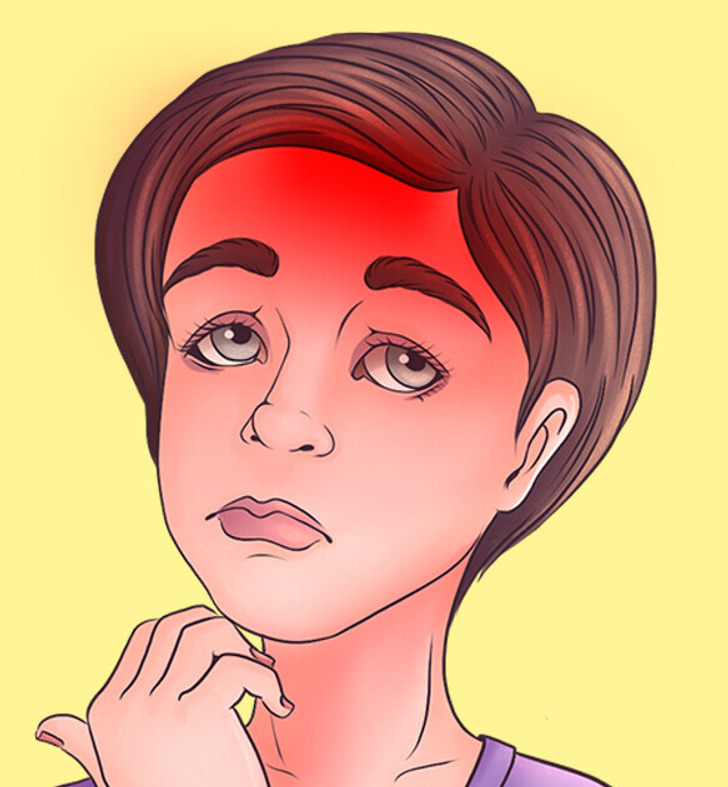

Some of the most concerning causes of severe headaches include stroke and brain aneurysms. These headaches often come on suddenly and with intense pain.
A hemorrhagic stroke can cause a sudden, severe headache. People with uncontrolled high blood pressure are at higher risk. Symptoms may include:
Since hemorrhagic strokes can cause severe brain damage, immediate medical attention is critical. Delayed treatment increases the risk of permanent damage or death.
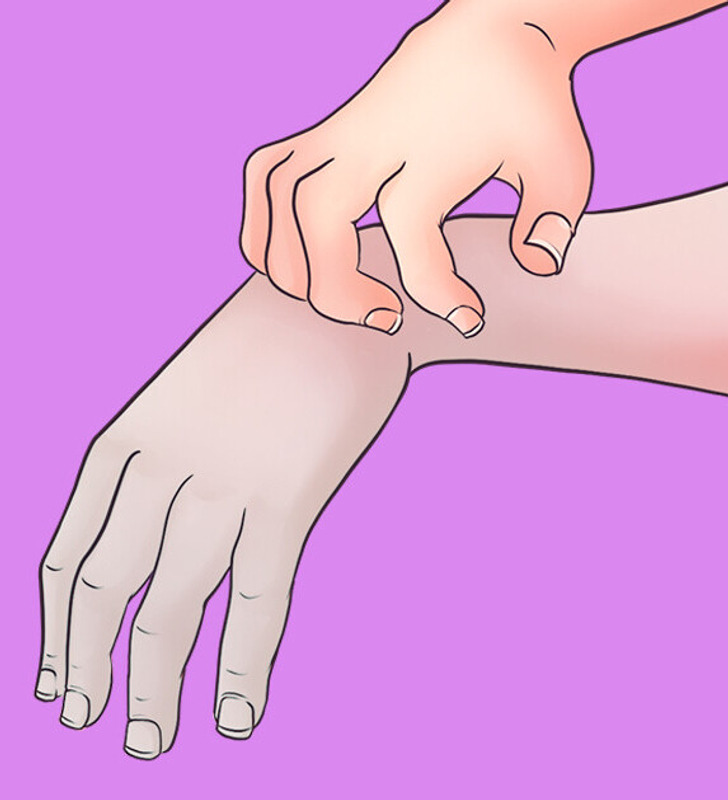
A stroke can happen suddenly and requires immediate medical attention. One of the most critical warning signs is sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg—especially on one side of the body. This can be a sign that blood flow to the brain has been disrupted, and even if the symptoms go away quickly, they should never be ignored.
Other signs of stroke include:
Additional warning signs can include double vision, drowsiness, nausea, or vomiting.
The best stroke treatments are only effective if given within three hours of the first symptoms. If a stroke isn’t recognized in time, patients may not qualify for these life-saving treatments.
If you suspect someone is having a stroke, act F.A.S.T. and use this simple test:
If stroke symptoms disappear after a few minutes, it may be a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or “mini-stroke.” A TIA is a serious warning sign of a possible future stroke.
Because symptoms go away quickly, many people ignore a TIA, but that can be a dangerous mistake. If you or someone you know has stroke-like symptoms, seek medical help immediately—even if they stop. Early intervention can prevent a more severe stroke in the future.











