“Pushing 60, Trying to Look 30,” Nicole Kidman’s New Bold Style Is Deemed Age-Inappropriate


Coffee, with its high caffeine content, can have significant effects on the human body. Upon consumption, caffeine quickly enters the bloodstream, stimulating the central nervous system and blocking the effects of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleepiness. Besides this well-known effect, there are some other curious outcomes.
Caffeine demonstrates efficient absorption within the human body, with its immediate impacts typically manifesting within 5 to 30 minutes of consumption and one sip can be enough. These effects encompass heightened respiratory and cardiovascular activity, augmented cognitive vigilance, and amplified bodily vitality. Duration of these effects may vary, potentially extending for as long as 12 hours, contingent upon individual factors.
Caffeine, acting as a stimulant substance, accelerates the transmission of messages between the brain and the body. Regardless of the substance, all drug usage inherently involves risks and lacks a universally deemed safe threshold. Thus, it remains crucial to exercise caution when consuming any form of drug.
The impact of caffeine varies from person to person, influenced by factors such as:

Similar to numerous other drugs, the development of a tolerance to caffeine is plausible. This adaptation entails acclimatizing to its bodily effects, consequently necessitating increased intake to yield comparable outcomes. Consequently, prolonged usage might engender a reliance on caffeine, both physically and psychologically, to maintain optimal functionality.
In the event of dependency and subsequent cessation of caffeine intake, withdrawal symptoms can emerge, such as:
Manifestations of caffeine withdrawal typically commence within 12 to 24 hours and may persist for approximately seven days.
According to a study from 2020, coffee was found to enhance performance by an average of 1.7%. While this might not seem like a significant leap, it’s certainly noteworthy, particularly for athletes operating at a moderately competitive level. An earlier study conducted in the UK highlighted that coffee consumers demonstrated improvements in reaction times, memory, and visual-spatial reasoning, with the degree of improvement correlating with the amount of coffee consumed.
It’s important to note that the primary contributor to these performance benefits is caffeine, which implies that coffee might not always be the optimal choice. A recent analysis conducted by the consumer group revealed that a medium cappuccino contains 66-325mg of caffeine.
Beans can make a difference. Standard robusta beans are higher in caffeine than arabica beans.

Some indications suggest that the long-term advantages of its mood-enhancing properties can be substantial. An analysis of observational studies in 2016 revealed that the consumption of caffeine was linked to a reduced risk of depression. Similarly, a 2010 Finnish study uncovered a comparable outcome associated with coffee consumption. Notably, in the Finnish study, the strength of this correlation diminished when individuals consumed other caffeinated beverages.
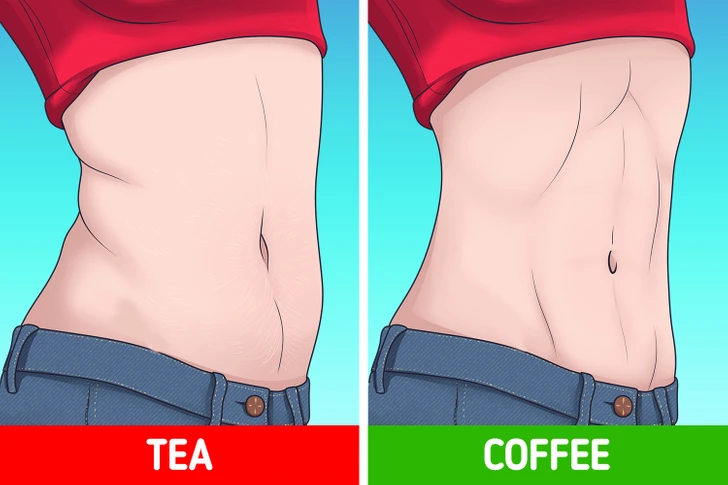
Consuming coffee just before exercising has been shown to enhance performance, fostering a sensation of increased endurance. This, in turn, can amplify calorie expenditure during the workout, potentially expediting weight loss. Numerous individuals opt to incorporate coffee into their pre-workout protein shakes, while others prefer to consume it black. Pre-workout consumption of black coffee can lead to heightened calorie burn both during and after the workout, alongside an improved utilization of fatty acids for aerobic energy.
Some sources suggest that 4 cups of coffee can elevate your metabolic rate by 3-11%. With an increased metabolic rate, fat burning becomes more efficient. Consequently, this attribute is highly beneficial for individuals aiming to achieve weight loss goals.
Antioxidants play a critical role in shielding the body from the detrimental impact of free radicals. Notably, the Western diet predominantly sources approximately 79% of its antioxidants from beverages rather than food.
Research conducted in Finland and Norway underscored coffee’s significance as the primary antioxidant supplier, contributing to approximately 64% of the overall antioxidant intake. Embracing an antioxidant-rich diet from various sources, including coffee, is essential for fortifying the body’s defense against harmful oxidative stress. This underscores the importance of integrating antioxidant-rich beverages like coffee into one’s daily dietary regimen.

Water retention, also known as edema, refers to the accumulation of fluid causing swelling. Caffeine, known for its diuretic properties, doesn’t get stored in the body. As a result caffeine is eliminated through increased urine production.
This diuretic effect aids in mitigating water retention, a common barrier to weight loss progress often characterized by feelings of bloating and sluggishness. By combating water retention, caffeine contributes to a more comfortable and effective weight loss journey.

Scientific evidence confirms that caffeine directly stimulates fat cells, prompting them to break down stored fat. Prior to being utilized and expelled through physical activity, fat necessitates this breakdown process. Additionally, coffee elevates adrenaline levels in the bloodstream, facilitating the breakdown of fats. Consequently, caffeine remains a key component in various weight loss supplements.
Moreover, the presence of Chlorogenic acids in coffee is known to suppress appetite, leading to reduced food cravings. This characteristic proves beneficial for individuals aiming to manage calorie intake. While raw (green) coffee beans serve as the richest natural source of chlorogenic acid, roasted coffee also retains this component. Notably, lighter roast profiles preserve a higher concentration of chlorogenic acid.
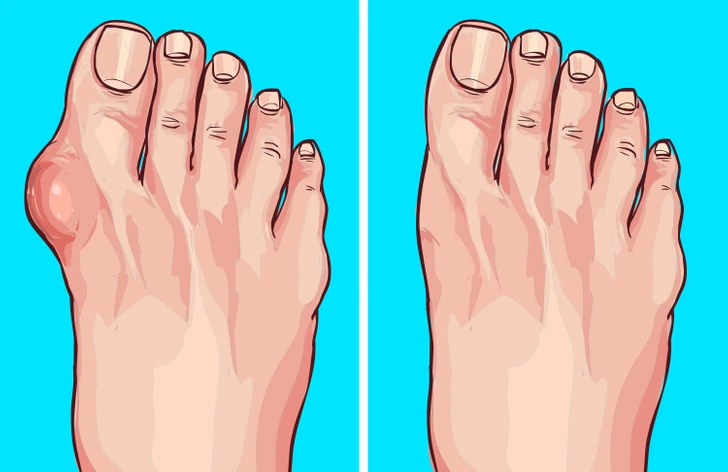
There’s positive news for men. Research indicates that higher coffee consumption is associated with a reduced likelihood of developing a particular type of inflammatory arthritis. Over a span of 12 years, a comprehensive study involving 45,869 male participants was conducted to arrive at these findings.
However, it’s crucial to note that individual health circumstances can vary, and the effects of coffee on health can differ from person to person.

Symptoms indicating excessive coffee consumption include:
Coffee, a beloved elixir, has woven itself into the fabric of daily life for countless individuals worldwide. Beyond its functional benefits, coffee often serves as a catalyst for connection, fostering intimate conversations and camaraderie among friends and colleagues.